Cash systems of capitalist and developing countries. Modern monetary systems
Modern monetary system includes the following elements: monetary unit; price scale; types of money; Em session system; State or credit apparatus. Part of The monetary system is the national currency system, although it is relatively independent. The monetary unit is a monetary sign established in the legislative order, which serves to compose and express the prices of all goods. The monetary unit is usually divided into small multiple parts. Most countries have been established decimal system divisions: 1:10: 100 (1 US dollar is equal to 100 cents, 1 pound sterling - 100 Pensam; 1 Indonesian rupee - 100 hay, etc.). The official scale of prices has lost economic meaning with the development of state-monopoly capitalism and the termination of the change credit money On gold.
As a result of the Jamaician currency reform of 1976 - 1978. The official price of gold and the gold content of monetary units canceled. The types of money that are a legitimate payment facility is mostly credit banking tickets, as well as paper money (treasury tickets) and a translating coin.
For example, in the USA in circulation there are: banking tickets at 100, 50, 20, 10, 5, 2 and $ 1 (release of banknotes of 500 and above dollars is terminated); Treasury tickets at 100 dollars; Silver-copper and copper-nickel coins of $ 1, 50, 25, 10, 1 cent. In the UK, there are banknotes in 50, 20, 10, 5 and 1 f. Art., Coins in 1 f. Art., 50, 10, 5, 2 penns, 1 and 1/2 Penny. They have walking old coins in 2 and 1 shilling, which in terms of cost correspond to the new 10 and 5 pens. If in industrialized countries, as a rule, government paper money is not produced in the narrow sense of the word (treasury tickets), then in some developing states They are common. So, in Indonesia, treasury tickets are issued by the advantage of 50, 25, 10, 5, 1 Sep, in India - in 1 rupee.
The emission system in developed capitalist countries means the issuance of banking tickets by central banks, and treasury tickets and coins - treasury in accordance with the legislatively established issuing law. The main channel of the emission of money in these countries is the deposit and check emission: an increase in deposits on customer accounts and, accordingly, the mass of checks serving the payment turnover. It involves commercial banks and other credit institutions. For example, in the United States, the right of release of banknotes is provided by the Federal Reserve System (Central Bank), and small-scale cash tickets, silver dollars and a translating coin - the Treasury. Characteristic features of modern monetary systems of industrialized capitalist states are: the abolition of official gold content, ensuring and reproduce a banknote on gold; the transition to non-removal on gold credit money, which are reborn into paper money; issue of money in appeal not only in order bank lending farms, but also to a large extent to cover state expenses (emission support is mainly government securities); predominance in cash circulation of non-cash turnover; Strengthening state monopolistic monetary management. In the late 1970s of the 80s, the majority of small states, including island, national monetary systems were created, the provision of sustainability of which is the most important condition Normal development of national economies.
8.1. US monetary system
The US monetary system in the XX and XXI centuries determined in many respects and determines the vector of the development of world monetary and financial systems.
In the USA until 1900, there was a system of bimetallism. In 1990, an act of a gold standard was published - the golden dollar became a monetary unit. In 1934, in the interests of the US silver industrialists, the stocks of precious metals and silver were replenished (according to the law - not over 25%).
For a long time banknotes released commercial banks. By law 1863, this right was provided to national banks subordinate to federal legislation. But the situation has been preserved because most of the banks have completed the requirements. According to this law, banks could produce banknotes in the amount of state loans purchased by them.
In 1913, a federal reserve system (Fed) was created from 12 emission banks located in different states. This decentralized system served as a central bank.
In the period of the global crisis of 1929-33. The USA acted in the USA. In 1934, the United States moved to a mixed gold and gold standard.
In 1944 at the UN conference in Bretton Woods (USA), the gold and foreign exchange standard was fixed (Bretton Woods Monetary System). As global currencies, along with gold, the dollar was recognized. The price of gold in dollars was appointed unchanged - $ 35 per troy ounce. The dollar has become a recognized world currency. In 1970, his share in the gold and foreign exchange reserves of all countries of the world was about 75%.
However, the number of dollars by 1970 exceeded the US gold reserves several times. In addition, high inflation took place in the United States, and there was a recession in the economy. The countries of the world began to intensively exchange dollars on gold. Then the USA August 15, 1971 refused to exchange dollars for gold. In response, Western countries refused to support the dollar, and the world switched to currencies with a floating course.
Currently, the US monetary appeal is determined by the Fed, the Ministry of Finance (Treasury) and commercial banks.
Fed represented by federal reserve banks issues banknotes - the main means of cash circulation. The Fed according to the law determines the usual and monetary policy of the United States.
The Ministry of Finance of the United States produces small tickets (treasury tickets) from 1 to 10 dollars, silver and exchange coins from nickel and copper. The emission of treasury money was up to 11% of the cash and money supply (mainly coins).
Commercial banks emit bills, checks, credit cards - Cashless money. They make up more than 80% of the money supply and are represented by bank accounts.
Deposit accounts to demand are played an important role in non-cash settlements.
Money circulation regulation is carried out mainly by Fed using the following main tools:
- regulation of money supply;
- accounting changes;
- state securities.
8.2. Monetary system FRG
Before the formation of a single state in Germany, various types of monetary systems were functioning with a predominance of silver monometallism. In 1871-73 After uniting lands, Germany moved to unified system Golden monometallism - the gold standard - Reichsmark (gold content - 0.3584).
At the time of World War I, the Golden Standard was canceled, and after the defeat of Germany, it was introduced the gold and foreign exchange standard (goldenness). During the period of the global crisis of the 1930s, this standard was canceled.
During World War II, Germany moved to the release of unsecured treasury tickets. After the war, Germany was divided by former allies into two parts: Germany and GDR. In May 1949, a gold frame standard was installed in Germany. In 1976, after the official cancellation of the IMF of the Golden Parity, the German brand lost and formal gold collateral.
Before the introduction of the Euro regulation of credit and money policy and emissions, the German Federal Bank was engaged in accordance with the legislation. He, regardless of the executive, planned monetary policy, money supply and inflation policy.
8.3. Japan's monetary system
In Japan (Monetary Unit - Yen) in 1897-1933. There was a gold standard (gold). With preparation for war and during World War II, he was canceled.
Modern cash in Japan serve as banknotes with a par value of 1000, 5000 and 10,000 yen, as well as coins with nominal 1, 5, 10, 50 and 100 yen. Cash emissions is carried out by the Bank of Japan. Cash is provided by the assets of the Bank of Japan, including the country's gold reserves (the largest in the world - over 400 billion dollars. In 2002).
In Japan, cashless cash circulation prevails. The Bank of Japan regulates the cumulative cash circulation using:
- regulation of money supply;
- accounting rate;
- state securities;
- preferential lending to commercial banks;
- regulation of the currency rate of the yen;
- gold and foreign exchange reserves;
- direct state aid commercial banks.
In the 1990s, the economy Japan experienced a long-term recession band (negative or close to zero GDP growth rates). The Bank of Japan to revitalize business activity conducted a policy of cheap loans (zero rate for commercial banks) and the policy of the understated course of the yen to support exports. As a result, at the beginning of the XXI century. There was a small increase in Japan's GDP.
Questions and tasks:
1. What is the main difference between the modern US monetary system?
2. What type of monetary system was in the United States in the year before last?
3. Who released banknotes in the United States in the nineteenth century?
4. When the United States switched to the monometallism system?
5. When the US dollar and why became world currency on a par with gold?
6. With what tools of the US Fed regulates the monetary market?
7. When and why the US abandoned the Golden Standard?
8. Who and what makes money in the USA?
9. What type of monetary system was in Germany in the year before last?
10. What is the name of the FRG monetary unit at present?
11. Is German dependent national Bank from executive?
12. Who and what makes money in Germany now?
13. What is the name of the monetary unit of Japan?
14. With which tools, the Bank of Japan regulates the monetary market?
15. Who and what makes money in Japan?
2.1. Organizational principles of monetary regulation
The organizational structure of the US credit and monetary regulation bodies, their powers and methods of activity are based on extensive and extensive legislation, which reflects the historical features of the formation, economic development of the country's economy and the country's monetary sphere. The control and regulatory activities of these bodies are largely intersect and duplicated, and this is one of important features Credit management organizations in the United States 1.
In the US, banks are divided into national, based on the license (charter) of the federal government, and the state banks operating on the basis of a license (charter) of the state government. This feature leads to a binary interpretation of the principle of two-level construction of banking systems adopted in most countries. Usually the term "two-level system" means that the first level is occupied by the Central Bank as the regulatory authority of the monetary system, and at the second level all other credit institutions are: commercial, savings, mortgage banks, etc. In the US, the two-level system includes federal backup system (Fed), national banks and banks of states. The US financial and credit system has another feature. The Fed is not only a central bank, but also at the same time a professional association of bank banks. All national banks are necessarily members of the Fed, which gives them some benefits and imposes obligations to fulfill certain requirements of the Fed. Story banks can be members of the Fed on a voluntary basis. But in any case, they are obliged to perform the instructions of the Fed. Respectively
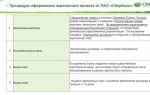
but, national banks form one level of the US banking system, and the banks are second. The principles of building a banking system of the USA are displayed in Fig. one.

Figure - US credit-monetary regulation authorities 1
Regulatory regulation is intended to perform the following tasks 2:
Ensuring the reliability and efficiency of the monetary system of its economic tasks;
Ensuring the sustainability of the credit system and the prevention of bankruptcy of commercial banks and other credit institutions;
Limiting the scale of concentration of capital capital in the property of few credit institutions, preventing the establishment of monopoly monitoring of these banks over the money market.
In the main organs regulatory regulation The US credit and monetary service is included several institutions.
1. Office of the Office of Comptoller of Currency Monetary Controller) (hereinafter - UKO). This structure in the treasury of the United States (Treassury Departament) is issued by issuing permits (charters) to create national banks, supervises them and conducts regular audits of their activities. Each National Bank is checked at least two times over three years and is obliged to submit reports to UKDO at least four times a year. UKO also considers applications about the opening of offices and the merger of banks.
2. The Federal Reserve System (Federal Reserve System) is the main economic regulation authority of the monetary sphere, the Central Bank of the United States.
The Fed has a wide range of administrative authority, which it uses for supervision and control over the activities of credit institutions. At the same time, the Fed conducts regulatory measures, which through the monetary scope has a great influence on the state and nature of the development of the US economy. The Fed Policy significantly affects the global economy as a whole. Therefore, the activities of the Fed are planned close attention not only credit organizations US, but also all countries of the world.
The Fed was established in 1913 to control at the federal level of cash circulation and banking activities. The entire territory of the United States was divided into 12 districts, in each of which a federal reserve bank was created, and together they form the Central Bank of the United States - Fed. Its modern status, the principles of the organization and the powers were under the influence of a number of laws.
Fed is federal institution, independent of the legislative and executive branches of power. This status allows its leadership to independently make monetary policy decisions. Fed independence is provided not only by the legislative guarantee of its status, but also to the procedures for the appointment of its leadership.
The Higher Fed Agency is the Board of The Federal Reserve, it is often called a Federal Reserve Board for brevity in English. The Council consists of seven members who are appointed by the President in coordination with the Congress every two years for a period of 14 years, in order to ensure the rotation of the members of the Council. The monetary circulation controller and the Minister of Finance cannot be members of the Council. The Council may include only one of the chairmen of the Federal Reserve Bank. If a member of the Council performed his post full time, he could not be appointed for the second time. From among the members of the Council, the President of the country appoints the Chairman of the Board of Governors for a period of 4 years. He can take his position several times. Since 1987, this position occupies A. Greenspan. In June 2004, he was once again appointed this post by President George Bush.
The authority of the Board of Governors Fed includes 1:
- change the norm of reserve requirements within the limits established by law;
- approval of accounting rates proposed by federal reserve banks;
- regulation of loans to federal reserve banks to each other;
- conducting supervision over federal reserve banks and checking their activities.
- election of the Chairman of the Board of Directors and his deputy for each Federal Reserve Bank from its Board.
An important and influential Fed authority is the Open Market Committee (Federal Open Market Committe) (hereinafter referred to as the FOMS) consisting of 12 people.
It includes members of the Board of Governors and five presidents of federal reserve banks, necessarily including the New York Reserve Bank. The Chairman of the FOMS is the Chairman of the Board of Governors of the Fed. The Committee is conducting trade in state securitiesand through the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) (hereinafter referred to as FXD) was established in 1933 and is one of the main institutions. financial system USA. The law provides for the mandatory federal insurance of deposits for national banks and - voluntarily - for state banks. The banks of the states are involved in the insurance and regulation system through the correspondent accounts mechanism that they must be kept in national banks. In 1934, when the FXD began its activities, deposit insurance in the amount of 100% was made in the amount of up to $ 2500. At present, all deposits of up to 100 thousand dollars should be insured, which most small depositors and depositors from the middle class have USA.
The FXD also conducts an assessment of the activities of credit institutions - their reliability, level of management personnel, compliance with the activities of banks with the requirements regulatory documents. Without ensuring insurance in the FKSD, the bank cannot begin its activities. The FSD on a regular basis also checks the activities of credit institutions and in the event of the need to participate in solving issues related to the discovery of branches, mergers of credit institutions, and in many other similar cases. The wide range of powers of the FXD makes it one of the most important institutions in the system of state regulation of the US credit system.
Banking Department of State (DEPARTMET OF BNAKING) (BDSH) issues licenses (charters) state banks for operations. In addition, the DBS issues instructions, conduct checks of banks, impose fines under certain violations, make decisions about the opening of offices and mergers.
Other credit institutions are also affected state bodies. Among them should be noted the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council and Securities and Exchange Commission (Securities and Exchange Commission), which have large powers and conduct large-scale regulation.
There are also non-governmental organizations conducting control over the activities of credit institutions created by industry or other principle. These include, for example, the American Association of Bankers, Association of Independent Banks, various committees clearing chambers etc. These organizations are developing equipment for operations and customer service standards, support contacts with authorities and press.
2.2. The role and functions of the Federal Reserve System
The Fed is endowed with the state of the monopoly of the issue in circulation of cash. IN modern economy Not only central banks, but also private commercial banks and other credit institutions create money. However, there is a clear division of rights between them. Commercial banks create cashless money when deposits are opening, issuing loans and conduct calculations by transferring money from one account to another. But the right of cash emissions is a monopoly of the Fed. She publishes cash in the form of banknotes and coins that manufactures treasury on its requests.
For the US economy, the growth of money supply is characterized, the value and structure of which is the result of a series of economic factors: general economic growth, income and scale levels of monetary credit operations. The number of cash, which occupy a small, but important place in the US economic life and serve as an influential element in the international economic position of the country. The number of cash required for the appeal is determined by economic practice when credit institutions fulfill the requirements of customers for cash issuance and make cash during them during banking operations. In modern conditions, cash payments are only 5-6% of the total calculation. The bulk of banking operations is carried out through the electronic calculation system, including remote operations with the help of cards and banking machines 1.
If it is necessary to obtain cash banks contact the Fed, which supplies them with cash, and during surplus - they give them back. The release of cash in appeal occurs under the obligatory provision, mainly - on bail state Bonds. Fed requires banks to make state bonds in banknotes in banknotes as to ensure the same amount. Unsecured cash in appeal are not available.
In the United States, banknotes are currently being produced by the dignity of 1.2, 5, 10, 20, 50 and 100 dollars. Of about $ 560 billion. Cash issued in circulation in 2004, almost two-thirds were billing bills. And about 15% - $ 50 bills. Most of these bills are outside the United States, since the Americans themselves are rarely used for cash bills above $ 20.
In principle, it is possible to issue a higher dignity banknote. Banknotes with a face value of 500, 1000, 5000 and $ 10,000. Were approved for emissions in 1918 and were intended mainly for interbank operations. They apply mainly in the period 1920s and 1930s. And used not only by banks, but also the population for which they served as a means of savings in the conditions of low reliability of the banking system. There was even a banknote of 100 thousand dollars. Purely for settlements between banks. Stroking the banking system after its reform in 1933 reduced the need for such large bills, and by mid-1940s. It became obvious that transactions of non-cash settlements confidently displacing these cash banknotes. In calculations and banking operations, large bills were replaced by checks, and the population ceased to apply cash for saving, preferred bank deposits and other assets that bring income in the form of interest. In view of these circumstances, since 1946, the release of new banknotes of this dignity was stopped, and in 1969 the Ministry of Finance and the Fed decided to remove them from circulation. All bills of listed dignity, which by that time returned to federal reserve banks were destroyed. Lost in the economy, the few bills of this class formally remain a legitimate payment facility, but currently they are so rare that they can be found only in numismatons or financial dealers. Thus, the largest bill that remains in circulation after 1969, became a banknote of $ 100. However, the Fed retains the right to issue all the nominal banknotes into the appeal, and the Treasury is the right to manufacture.
The dollar banknotes of major dignity is appropriate to recall in connection with the introduction of January 1, 1999 in 12 EU countries. Introduction of cash in the form of banknotes began with 2001. Cash euro is issued by banknotes in 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 500 euros and translating coins in 1 and 2 euros, as well as 1, 5, 10, 20 and 50 euro satellites.
Some experts in the United States fear that the euro can fasten the dollar in world calculations, especially in transactions using major bills. The dollar may lose a competitive advantage and as a means of accumulation for the population of some countries, since there are 200 and 500 euros in the euro system for this, while bills above $ 100 does not exist. To hold the positions of dollar bills in the world circulation, they offer to resume the issue of banknote in total $ 500. It is noted that such bills will be eagerly applied to wealthy groups of population as a means of calculations and accumulation. All these arguments are primarily to use dollars in developing countriesah Asia, Latin America and countries with transition economyFor which the "dollarization" of the economy is characteristic.
Opponents of the issue in circulation of 500-dollar bills indicate that they are not needed for internal circulation in the United States. Benefits from the convenience of their use will be available not so much to honest citizens as violates of the law interested in large bills, which are more convenient to use when laundering criminal income, tax evasion and other illegal operations. Thus, opponents consider, the release of 500-dollar bills will be the service mainly for the shadow business and a frank crime, whose needs of the Fed there is no need to take care. In their opinion, a denomination of $ 1,00 is quite sufficient for calculations, and for accumulation, and the position of the dollar in the world is determined by more important factors that are based on strength and stability. political system The United States, a high level of development of the American economy, the power and perfection of the financial system, as well as on the fact that the US authorities do not limit the periods during which dollar bills issued into circulation are mandatory to receive with all monetary operations On their territory. This forms a relation to the dollar in the world as a monetary asset, the reliability of which is almost eternal, which serves as an important factor in its preference to other currencies.
The Fed conducts a large amount of settlement operations, acting as a compulsory mediator between banks and other credit institutions. Together with their departments and offices, federal reserve banks form an extensive system of calculating management in the credit and monetary sphere. In total, there are 25 branches and 48 regional offices of federal reserve banks, each of which provides a wide range of banking services for credit institutions, including storage and processing of banknotes and coins, processing checks, food coupons, as well as other types of payments and financial services. As financial agents of the US government, federal reserve banks and their branches are treated with a large amount of various securities in the form of savings bonds, treasury notes and bills. Regional offices provide services mainly in the processing of checks. For example, in 1996, 64 billion checks were discharged in the United States for a total of 75 trillion dollars, i.e. Each average American family per month wrote about 25 checks 1.
According to the system of direct deposits, the Bank on behalf of the enterprise writes off from his account the amount of monthly wages Employees and forwards money to an automated settlement chamber (hereinafter - armp). Within the framework of the Fed, there are several ARPs that provide clearing services to all deposit institutions that provide information in the form suitable for automatic processing. In addition, there are several private armp. All of them are currently in an armp system acting on the scale of the country. Having received funds from the bank, the settlement chamber distributes this amount between banks in which employees of the enterprise hold their accounts, and those banks produce appropriate accruals on their accounts. Employees of enterprises regularly send notifications with an indication of the accrued amounts and states of their accounts. Using this system in the United States, payroll is accrued with more than 80% of employees.
When listed wages, cashless money is moving. Next, the Bank analyzes the demand of customers and forms its cash needs, taking into account the fact that cash transactions are carried out mainly not in the premises of the bank or its offices, but on a large scale are performed in remote mode through an extensive network of banking machines. Automatic banking services Burnt large scale in recent years. They are available to each bank depositor and are provided with help bank cardswhich are issued to the client when opening a deposit. You can contribute to the automaton or pay interest, to remove some amount of cash from the account, to transfer the contribution from one deposit account to another, make payments on a bank loan or for utilities, Check the status of your account. All these operations allow banks to significantly expand the client's circle and the service time range - most banking machines work around the clock. Since all ATMs are associated with the general electronic system Bank, their reliability is fully secured, and bank employees have the ability to constantly monitor these operations and manage them. In the United States there are about 100 thousand ATMs, combined about 150 systems related to a nationwide network.
2.3. Economic methods of credit and monetary regulation. Money mass and its aggregates
Credit regulation covers not only cash in circulation, but also the entire money supply of the country, the changes in which lead to the derate activity of the business activity and the nature of the economic development of the United States.
Since the Fed, in fact, is the main and only issuer and the "regulators" of the money supply, then for its measurement since 1980, measures were established on the suggestion of money, which are called monetary aggregates. Their magnitude for September 2003 looked as follows 1:
M1 \u003d Cash + Traveler Checks + demand deposits + + other check accounts (M1 \u003d 1178 billion dollars)
M2 \u003d M1 + Urgent deposits worth up to 100 thousand dollars + savings accounts and deposit accounts money market + PAIs in mutual funds of the money market (private owners) + short-term redemption agreements + short-term deposits in Eurodollara (M2 - 5378 billion dollars).
MH - M2 + term deposits in the amount of over $ 100 thousand + PAI in mutual funds of the money market (corporate owners) + long-term converse redemption agreements + long-term deposits in Eurodollara (MH 7800 billion dollars).
L \u003d MD + short-term treasury bills + commercial securities + savings bonds + bank acceptances (L \u003d 9000 billion dollars).
Another indicator of the amount of money in the economy is the monetary base - MV. The monetary base includes the amount of cash, i.e. Banknotes and coins - C (CASH, CURRENCY) and the total amount of banking system reserves - K (Reserve). The procedure for calculating MV, in comparison with monetary aggregates of money supply - M1, M2, MH and L, is much simpler, since the volumes C and K are determined directly to the Fed, while the components of the monetary aggregates are determined by commercial banks and can move from one category to another.
However, due to the fact that the prevailing part of cash issued in the United States is in circulation outside their borders, the Fed uses data on cash in the cash desks, safes of banks and other credit institutions.
Methods of credit and monetary regulation are based on the use of three tools that have a strong impact on the overall state of the monetary sphere, and through it - and on the state of economic activity. These include:
- change of the norm of mandatory reserves for commercial banks and other credit institutions;
- change in the rate of lending to the Fed;
- Fed operations on the open market.
These tools give a significant economic effect, so their application is considered to be the main content of the Fed Credital Policy.
Changing the norm of mandatory reserves serves as the most radical method of regulation. The duty of commercial banks to store a certain percentage of funds from the amount of deposits on special reserve accounts of the Fed was established by law in 1933 in order to ensure the liquidity of banks and prevent their collapse in the event of a sudden seizure of funds by depositors. The limit norms of mandatory reserves are established by law, and the Fed has the right to change them in the designated framework.
In practice, the Fed is very rarely changing the norms of mandatory reserves, since this tool acts very significantly and can reduce or increase the money supply on a large scale. The principle of credit expansion proves that the monetary mass after the initial deposit is incremented in proportion to the magnitude of the banking multiplier, which mathematically expressed as the attitude of this deposit to the norm of mandatory reserves. Therefore, the change in the norm of mandatory reserves leads to a multiple increase or decrease in the money supply. For example, with a reservation rate of 10%, the multiplier is 10. Theoretically, this means that when lending to the Fed of a commercial bank in a volume of 100 dollars. The banking system as a result of a consistent deposit creates a total amount of deposits $ 1,000 and the amount of mandatory reserves of $ 100. In fact, credit Issued by the Fed Commercial Bank returns to it in the form of mandatory reserve deductions.
In reality, the value of the banking multiplier is significantly less than the calculated due to the effect of attenuation and cross lending, but it is still large enough and acts effectively. Moreover, the changement of reserves is so effective that for small changes in the demand of the money needed extremely small adjustments to the norms of mandatory reservation - hundredths and even thousandths of percent. This effect is achieved during operations on the open market, so that in the usual FRS situation there is no need to resort to direct change in the norm of mandatory reserves. Therefore, the Fed used this tool only during periods of economic crises, for example, in 1950-1970. one
In 1980, the Law on Monetary Control (Depository Institutions Deregulation and Monetary Control of 1980) has adjusted the backup requirements system. Requirements for the need to keep backup deposits in the Fed were distributed practically to all credit institutions. Until 1980, the Reserve Coverage requirement was only related to the banks of the Fed and applied to all deposits in these banks. After the adoption of the law, all US deposit institutions (commercial and savings banks, loan-savings associations, credit unions, American branches and agencies of foreign banks, as well as other credit organizations) must comply with the established Fed regulatory requirements and keep your own reserves in the form of cash cash in your institution and in the form of deposits in federal reserve banks 1.
The terms of deposits to ensure the reserve coating are limited by three types: transaction accounts, non-personal deposits (deposits belonging to not a separate person, but an institution) and obligations to accounts in Eurodollara. New law eliminated the requirements for the backup support of personal savings and term deposits. This became possible due to the fact that the insurance system of deposits by credit institutions in the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation has shown its reliability. In combination with other measures to protect the rights of depositors and taking into account the level of development of the American banking system, the position of personal savings and urgent deposits has become quite strong. The release of these types of accounts from the mandatory reserve coating in the Fed is aimed at reducing bank costs when working with such accounts, an increase in their profitability, and thus stimulates the growth of personal savings.
The law of 1980 provided the Fed the right to change the reserve requirements for transactional accounts, on non-personal urgent accounts, as well as on the obligations (liabilities) of the US deposit institutions in relation to their foreign affiliates and other foreign banks.
For transaction accounts, limits from 0 to 14% are installed. In this framework, the Fed applies the standard of reserve liabilities in the amount of 3% for transaction accounts of a certain amount and 10% for larger accounts. The limits of reserve requirements for nonertial urgent accounts are set from 0 to 9%, and in this framework of the Fed can make changes to the timing of their repayment. For reserves in pure (net) borrowings of deposit institutions from foreign lenders (deposits in Eurodollara) limits are not provided. Since 1990, the Fed has made equal zero standards for reserves on nonertial and Eurodollar bills, i.e., no deductions to reserves applied.
The limit of the total amount of deposits is being revised annually, the requirements for the reserve coverage in the amount of 3% are applied. Such a revision is necessary as income and deposits have grown. In 2001, the accounts of 3% were used for accounts to $ 60 million, and more than this value for accounts - 10%.
In the mechanism of action of the mandatory reserves, the main thing is the absolute amount monetary resourceswhich should be supported by a commercial bank or other deposit institution in a reserve account in the Federal Reserve Bank. It must comply with the established standards standards.
In the United States, the composition of reserve assets that can be used to meet the reserve requirements, only two types of monetary assets are included. This cash cash (i.e., banknotes and coins stored in the cash desks and safes of credit institutions) and reserve accounts in federal reserve banks. Since funds in reserve accounts are stored in federal reserve banks, they received the name of federal funds.
Since banking volumes do not allow to maintain current reserve requirements daily, the procedure for which reserves should be maintained at a given level during the 14-day period. It is called a period of maintenance and is determined by a special technique.
The amount of reserve accounts in federal reserve banks and the part of the cash cash, which is commonly used for reserve needs, is called total reserves. Total reserves are divided into two parts. Their part of them is a mandatory reserves, the amount of which is determined by the current standards in the amount of specific deposits and other obligations of deposit institutions to be reserved. The second part of the reserves is excessive reserves, the value of which is equal to exceeding the actual reserves above the required. Obviously, banks are unprofitable to have redundant reserves, since it limits their ability to make active credit operations. But the bank cannot allow the deficit of reserves, that is, the states when the value of actual reserves is less than the required reserves required by law. In these cases, fines are imposed on deposit institutions.
Reserve accounts in federal reserve banks are interest-free. Therefore, credit institutions that are holders of these accounts are not interested in the occurrence of excessive, and even more so that these excessiveness make significant sizes. Therefore, federal funds trade: credit institutions that have a lack of reserve accounts, buy surplus from their partners. These operations are carried out regularly, since most of them relate to the category of short-term and even one-day (overnight). The interest rate on operations with federal funds is of great importance and serves as one of the main landmarks for the credit system and the entire economy.
Federal Funds Rate (Federal Funds Rate) is the main indication of the interest rate on the interbank loan market, which sells unnecessary reserves of commercial banks in the accounts of federal reserve banks. The market rate of interbank loans in which commercial banks buy each other free funds called the current or effective bid Federal funds (Effective Federal Funds Rate). It changes daily depending on the state of the loan market. The Fed itself in the process of buying and selling credit resources of federal reserves (funds) does not participate and, moreover, it does not even establish the tough value of such loans. The Fed Policy here is rather recommendatory in nature and is carried out through the establishment of a bet on federal funds, which serves as a guideline for the interbank loan market.
This bet, installed by the Fed, is called the expected or target bid of federal funds (Expected, Intended or Target Federal Funds Rate). Announced a change in the rate, the Fed makes it possible to understand commercial banks, which level of the value of interbank loans (actually the amount of money supply) will arrange the Fed, based on the analysis of the current state of the national economy.
The magnitude of the interest rate on operations with federal funds is established centrally. This right belongs to the Board of Managing Fed. Until 1994, the time of establishing a new rate was a service secret, since it is one of the Fed credit-monetary policy tools designed to influence the amount of money supply. Now the Fed has changed this rule and announces the upcoming revision of the federal funds rates to give participants in the credit market the opportunity to prepare for future changes. But the size of the new bet is not declared in advance, since it remains the subject of coordination at the meeting of the Board of Governors. Nevertheless, the direction of the upcoming changes is usually quite obvious, since it is dictated by the state of the economy in this moment. For example, in a decline in the US economy in 2001, the Fed consistently reduced the bid on federal funds 11 times from 6.5% at the beginning of the year to 1.75% at the end of the year.
Over the past decades, the value of mandatory reserves in the monetary system has changed radically. Their role as a means to ensure the liquidity of credit institutions and the guarantor of sustainability in sudden seizures of the funds with depositors significantly decreased, since these tasks are successfully implemented through the deposit insurance mechanism. At the same time, their meaning as a means of credit and money regulation has sharply increased. This allows not to resort to changes in the norm of mandatory reserves. Through the magnitude of the interest rate on federal funds and everyday changes in the amount of funds in the accounts of mandatory reserves, it turns out to be a fairly effective impact on the state of the credit system, the amount of money in the country and on business activity. Changes in the state of mandatory reserves are closely related to the use of other monetary policy tools: changes in the accounting rate and operations in the open market.
One of the most actively used regulatory tools is the change in the Fed lending rate. Discount Rate is a rate of interest determining the cost of loans provided by the Fed to commercial banks.
In practice, these operations are carried out through federal reserve banks. In addition to the lending rate, each federal reserve bank can determine the volume of lending to commercial banks, establishing the so-called discount window (Discount Window). The meaning of the expression "Discount Window" characterizes the difficulty of obtaining a loan from the Fed: this does not happen automatically, "through a widely revealed door", and on the contrary, it is a complex procedure that is carried out through the "narrow window" and in many cases may end with refusal. Regulation of the supply of money through the volume and cost of refinancing is called the discount policy of the Fed, which is historically preserved since the time of accounting or discounting bills of commercial banks. In modern conditions, the value of the Fed Account is perceived by society not as much as the loan price for commercial banks, how much as a given credit system is the minimum level of interest rate, which she should adhere to.
The Fed Decisions on Accounting Changes are made quite often - several times a year - usually due to the current state of economic activity for its incentive or deterrence. The Fed Account is considered one of the main indicators characterizing the state of the economy. It stands in a number of such indicators as GDP growth rates, inflation, unemployment, federal budget balance and balance of payments. The Fed Account serves as a tool for state influence on the dynamics of these indicators. Any change in the Fed account is immediately discussed in the press, commented by specialists and politicians.
Since the Fed Account is closely related to other bets, its size is set at the level corresponding to the general direction of the Fed monetary policy. The change in the Fed account is usually occurring simultaneously with a change in the rate of federal funds or it should be immediately after that and, as a rule, remains a constant similar period. Therefore, in 2001, the Fed account was subjected to changes 11 times and was reduced from 6.5% in January to 1.75% at the end of the year. one
Changes in basic accounting rates is an effective tool for regulating the amount of money supply, combining the efficiency of the action and determination of the strategic goals of monetary policy. An indicator of the status of money supply is usually the magnitude of the three main rates, according to which funds are borrowing by commercial banks for a short time.
Discount policy is especially important in periods of economic and financial crises as a means of maintaining the sustainability of the monetary system - at the moments when the liquidity of banks and other things deteriorates. financial institutionsMainly because of the collaborators in the stock market. In these situations, the importance of the Fed as a central bank is emerging: it acts as a bank of banks and advocates the creditor in the last instance.
Currently, banks rarely appeal to the discount window, since the procedure for obtaining loans is accompanied by checking the Fed of their activities, and banks prefer to borrow monetary resources in the market of interbank loans at the federal fund rate. For this reason, the level basic rates Fed - rates on federal funds and accounting rates - serves mainly for the impact on the state of economic activity through the monetary system and the securities market. Reducing the Basic Fed rates are made during periods of reducing business activity and serves as a signal for a total reduction. interest rates in the country. This leads to cheaper bank credit, as well as to facilitate lending conditions through the debt securities market. Such a policy is usually called the policy of cheap money ("Easy Money"). Comparative cheapness and availability of a loan leads to a certain increase in business activity and helps to overcome economic crises. It also contributes to the increase termal cost Shares due to a decrease in the basic interest rates. In addition, the cheapening of bank loans stimulates the growth of investment in shares, thereby increasing economic activity.
When the forces of cyclic lift act overly actively and there is an increase in inflation rates, the Fed resorts to increasing the base rates, submitting a signal about the need to rise in prices for a loan. The growth rate of interest limits the loan, contributes to a decrease in the exchange rate of shares and leads to restraining business activity. Such measures are called deflation policy. They are considered as a means of preventing the crisis and are applied in the conditions of "overheating" of the economy.
An example of the Fed discount policy can serve as its actions in recent years. From mid-1999 until the end of 2000, the Fed raised the interest rate to combat the overheating of the economy, and in 2001 he lowered them to fight the crisis.
In modern conditions, a very effective means of regulation serve operations on the open market. For the operational impact on the Fed's money supply, operations with securities, which are carried out almost daily, and, consequently, there are continuous changes in the bank's balance sheet - its liabilities and assets. Buying securities on the market, the Fed increases the amount of money supply in the country's economy, selling - on the contrary, reduces the money supply, as if "communicating" unnecessary money in their liabilities. Therefore, the dimensions of the backup requirements should also be changed. In this way, through the operations in the open market, the Fed affects the structure of bank's money resources, encourages it to issue new loans or, on the contrary, limits its capabilities in this area.
Operations in the open market with securities produces a FOM, choosing the US Treasury Treasury (Treasury Bills) for 91 and 180 days) and long-term treasury obligations (notes or bonds (Treasury Notes or Bonds), as well as government Bonds (Governments Bonds). These investment objects are selected for two reasons:
Fed does not invest in corporate papers to avoid conflict of interest;
The market turnover of government securities is so large that even large transactions do not affect their quotes significantly, that is, the correspondence of return on these securities level of the accounting rate is a consequence of changes in the money supply, and not direct demand for securities.
Indeed, the participation of the Fed in the purchase of securities boulders affects their price:
1) the demand increases, prices grow and the yield is reduced;
2) At the same time there is an increase in money supply, an increase in demand for investment (an increasing demand of money in securities), as well as an increase in prices and a decrease in yields with the simultaneous offer of money in the loan market, which also leads to a decrease in the rate.
In fact, the Fed operations on the securities market are a flexible and operational instrument for regulating the money supply, which include the main advantages of which include:
A fairly effective mechanism for regulating the money supply;
Full control of the Fed volume of purchase and sale of securities;
RESOLUTION OF MAKING RESEARCH AND RECOMIBILITY OF RESULTS.
Fed operations with government securities should not be considered as a loan to the government. The US legislation does not provide for direct provision of government loans by the Central Bank. All government revenues and expenses are regulated through the budget mechanism. The coating of the state budget deficit and the finding of the missing funds are carried out by issuing government securities (treasury bills, bonds, etc.) through the Ministry of Finance. Federal reserve banks participate in the placement of these securities and then use them as a tool for regulating the monetary sphere through the operations mechanism on the open market.
Operations in the open market Fed holds daily. But reports on these operations are published after the end of the next quarter, so commercial banks and other credit institutions do not know the goals of the Fed and actually act as passive players. Being related agreement with the Fed, they are forced to follow the line held by it. The consequences of these operations lead to constant changes in the magnitude of the reserves that commercial banks must support, and thus the Fed affects their lending opportunities. The total purchases and sales of government securities within operations in the open market is in recent years an average of $ 400 billion a month for purchases and as much on sales. The skillful management of these operations allows the Fed to effectively influence the activities of banks and credit institutions.
Conclusion
In the course of the study, the objective of the work was achieved - the monetary system was analyzed and the state of the monetary policy of Russia was investigated.
Under monetary policy, the combination of events undertaken by the government in the monetary sphere in order to regulate the economy. It is part of a common macro economic Policy. The main ultimate goals of monetary policy: sustainable growth rates of national production, stable prices, high level of employment of the population, balance of balance of payments. From their aggregate, you can distinguish the priority goal of monetary policy - stabilization of the overall level of prices.
Alking the finite intermediate targets. They are the volume of money supply and the level of interest rates.
Carries out monetary policy Central Bank of the country.
The measures of the Central Bank on monetary regulation of the economy are designed to ensure its stabilization at a low level of inflation and unemployment. Monetary policy can be aimed at stimulating monetary emissions, i.e. Expansion of the total amount of money supply in circulation (credit expansion), which gives the effect of some revitalization of the market situation in a decline in production. It can be directed to the restriction of monetary emissions, i.e. On the reduction of the amount of money in circulation (credit restriction). This option of monetary policy is usually used by the central bank during the periods of economic boom and in cases of signs of "stock habit". Credit restriction in the context of increasing production growth rates is designed to ensure the containment of "overheating" market conditions. The policy of credit expansion on the contrary is used to "swinging" market conditions and is usually applied during periods of crisis and decline in production. It is often combined with the scarce financing of the country's economy and leads to the exacerbation of inflationary processes.
In carrying out activities on monetary regulation of the country's economy, an objective contradiction between the task of combating inflation and the problem of incentive is inevitably arises. economic growth. therefore money-credit policy The Central Bank should be most closely linked to the state investment and financial policy and is complemented by a flexible system of tax regulation of the economy.
Specific methods and monetary policy tools Central Bank Defined by law on the Bank of Russia and are distinguished by a large variety. The central bank provided the broadest possible authority and complete independence on the choice of methods and activities on monetary regulation of the country's economy under current legislation.
State regulation of the monetary sphere can be carried out by how successful only if the state through the Central Bank can affect the scope and nature of the activities of private institutions, since in a developed market economy they are the basis of the entire monetary system. This regulation is carried out in several interrelated directions.
State control over the banking system aims to strengthen the liquidity of financial and credit institutions, i.e. Their ability to meet the requirements of depositors in a timely manner (primarily due to the accounting (discount) policies, operations in the open market, establishing the norms of mandatory reserves). These same measures are applied by the state for compression (expansion) of the money supply.
The public debt management is the direction of state regulation in the conditions of chronic budget deficits, which lead to an increase in state debt (external and internal). With an increase in internal public debt The impact of the state loan on the loan capital market increases. To do this, the Central Bank uses various methods of public debt management: buys or sells government obligations; changes the price of bonds, the conditions for their sale; In various ways, their attractiveness increases for private investors.
Methods of monetary policy are divided into two groups: common (influence the loan capital market as a whole) and selective (intended to regulate specific types of loan or crediting individual industries, large firms, etc.).
Thus, monetary policy is conscious monetary control in order to maintain economic stability, minimal inflation, maximum employment. For this, monetary policy has an impact on the amount of money supply, controlling and managing the amount of cash reserves in banking system generally.
The United States has developed a highly organized and effective monetary regulatory system, which has a strong impact on the economic development of the country. The regulatory authorities of the monetary system in the United States are characterized by a complex system of organizational construction and to a certain extent duplicate each other in practical activities. Despite certain costs of such a structure, it ensures effective control over the activities of many credit institutions in the country.
The United States has an effective regulatory system that is conducted by the Office of the General Controller, the Federal Reserve, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation and other bodies.
The main body of economic regulation of the monetary system in the United States is the Federal Reserve - Fed. It is organized as a central bank and at the same time as the highest body of the professional association of American banks, which includes national banks and banks.
Fed belongs to a monopoly on the release of cash. Fed organizes cash flow. From about $ 550 billion in 2000, more than $ 300 billion were in circulation outside the United States mainly in the form of $ 100 bills and $ 50.
For exposure economic methods The Credit Sphere and the US economy, the Fed uses changes in the norm of mandatory reserves, changes in the accounting rate and operation on the open market. The integrated influence of these tools, the use of each of which has its own characteristics, makes it possible to strengthen the sustainability of economic development in the United States, reduce the depth of crises and restrain excessive growth, generating inflation.
The Fed extremely rarely resorts to changing the norm of mandatory reserves, since such actions would lead to too sharp changes in the amount and structure of the money supply and overly strongly affected the state of the economy. Currently, the main norm of mandatory reserves is 3% of the deposits of deposits entering bank accounts.
One of the most actively used tools of credit and monetary regulation is changes in the Fed Account. It not only determines the cost of obtaining a loan by commercial banks from the Fed, but also performs a guide function for the entire credit system, affecting the state of the bank loan and on the operations in the securities market. The value of the accounting rate is closely related to the rate of federal reserve funds, which serves not only by a practical tool of banking operations, but also an important guideline in determining the interest rates and securities courses.
An important tool for credit regulation is the Fed operations on the open market. Purchase and sale of government bonds in Fed operations with commercial banks and other credit institutions serves as a means of exposure to the possibilities of bank lending banks and ultimately affects the amount of money in the country.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Antonov N.T. Bessel MA Cash circulation, credit and banks. M. 2000.
2015-01-27
Monetary system monetary system Monetary and banking system of Russia
Agapova T.A., Sergina S.F. Macroeconomics. Tutorial -M.: MSU. M.V. Lomonosov. - M.: DIS JSC, 2001.
Anikin A. US economy at the outcome of the century: the results of the problem // MEMO - 2000. - No. 11 - pp. 27 - 46.
1.1 Consider the monetary system of the state
The monetary system is a form of a state organization. cash circulation.
The following main elements can be distinguished in the monetary management organization: monetary unit, types of money, price scale, form monetary emission. Specific form of a piece of piece money, montometallism and bimetalism, undeveloped paper and credit money, determine depending on the historically specific filling of the elements of the monetary system, 1.
Monetary system, like any system, consists of a number of elements. The principle of the organization of the monetary system is the first fundamental element.
The rules that the state is guided by the country's monetary system is called the principles of the monetary system.
The following principles of the monetary system of market type are distinguished:
forecast monetary turnover planning;
credit nature of monetary emissions;
elasticity and sustainability of money circulation;
relative freedom of the central bank and accountability to its parliament;
security issues manufactured in circulation:
granting funds to the government only in lending;
supervision and monetary control;
comprehensive use of credit regulation tools (currency intervention, mandatory reserves, accounting
functioning on the territory of the country only national currency 2.
Consider the elements of the monetary system 3:
The monetary unit is a monetary sign approved by the legislative, which is necessary for the compulsion and expression of prices of goods; The monetary unit is the money name used in this state (ruble, dollar, Tugrik, Yen, Pound, Bat, etc.) or the name of the money in the international monetary system (euro, SDR, etc.). All monetary units are divided into smaller elements: a dollar or euro is equal to 100 cents, the ruble is 100 kopecks.
Types of money that are a legitimate payment facility - credit banking tickets (non-cash and cash), barn billarn coins, paper money (treasury commitments and tickets);
The types of money currently available is the result of the historical formation of monetary systems in the specific national conditions of the state or the group of states. At this time, generally distinguish cash (paper, translating coins and credit) and cashless money (records in bank accounts) (Fig. 1).
Species and character of money in cash and national systems Characterized by the degree of development of trade economic and credit relationships in the state or in the group of states. Cash and cashless money will be easily flowing into each other. Cash flows into non-cash (on bank accounts), and non-cash - in cash (from bank accounts). Cashless money in the modern monetary system reaches 80-95% of the overall amount of money economy;
Fig. 1. Types of money in the real system of money circulation 4
- Money mass - the amount of non-cash and cash, and in addition, other means of payment;
The emission system is the procedure for emissions of banking, as well as treasury tickets by treasury and central banks, as well as emission channels; Emission operations (transactions for the withdrawal of money from circulation and their release) are carried out by central banks (banknotes - banknotes), treasury (state executive), producing small paper-money marks.
Monetary policy - represents a set of monetary instruments (norms of reserves, parameters of money supply, credit periods, percentage rate, refinancing rates, etc.) and monetary regulatory institutions (Ministry of Finance, Central Bank).
The type of monetary system directly depends on the form of money functioning - marks of value or full-fledged money. In the course of the development of monetary relations and forms of money and two types of monetary systems were formed (Fig. 2.).

Fig. 2. Typology of cash systems 5
The metallic monetary system is a system based on metal money from the inner (real) cost, including mono- and bimetallic.
Monometallism is a monetary system at which one money metal acts as a universal equivalent. Historically developed monometallic monetary systems were based on silver, copper, gold. Copper monometallism is presented in ancient Rome in 5-2 seconds. BC. For a long time in Russia, copper money was the database of money circulation. As a result, Cankrin's monetary reform (1843-1852) in Russia, silver monometallism, in India (1852-1893), in Holland (1844-1875), in China, has existed until 1935.
Bimetallism is a monetary system, in which the role of the universal equivalent is fixed between two noble metals (traditionally gold and silver), it is supposed to be a smooth coin of coins from both metals and their free appeal. In the conditions of bimetallism, the correspondence between silver and gold coins is determined depending on market value Cash metals. This system existed in 14-17 centuries.
Three types of bimetallism are known:
Double currency system - in this case The state fixed the correspondence between metals, and the chasing of silver and gold coins, as well as the admission by their population, was produced under this ratio;
The system of parallel currency - the correspondence between silver and gold coins was approved by spontaneously;
The monetary systems developed on metal equivalents passed in their development following steps:
bimetallism → Silver monometallism → Golden monometallism.
Since the amplification foreign Economic Relations demanded that they serve them national currencies Stability, the use of the Gold Standard system (gold monometallism) was determined by the formation and development of a single global market. One of the direct prerequisites for the application by the countries of the Golden Standard was the accumulation of gold reserves.
Depending on the nature of the exchange of banknotes on gold distinguish the following types of gold standard: gold, gold and
gOLD SUPPLY (gold).
For the goldstand standard, the unobstructed sale and purchase of gold coins on banknotes ( credit Tickets at a fixed rate, i.e. Gold coins and banknotes are treated on equal. As a fundamental form of monetary management, the gold-based standard was enshrined by international agreements at the Paris Conference in 1867, where gold was recognized as the only form of global money.
The refusal of gold as the base system base is carried out gradually. In the process of monetary reforms 1924-1929. Return to the Gold Standard was carried out in two cut-off forms - gold and gold standards. Gold, displaced from retail turnover, does not stop consumed in the internal and international wholesale trade, but in the form of ingots - the golden standard. It is characterized by the exchange of banknotes on metal ingots, as a rule, weighing 12.5-14 kg.
In Denmark, Germany, Austria was used a gold-based standard (gold walled), i.e. banknotes are not exchanged for ingots, and in order to acquire gold, it is necessary to exchange a national monetary unit (banknote) for a certain number of currency (motto) of that state in which had a gold-based standard, and the already specified currency exchanged for gold. In this way, the currencies of some countries were raised dependent on the currency of other countries.
The gold and gold and gold standards were issued by the agreements of the states achieved at the International Economic Conference in Genoa in 1922 this conference and determined the status of a reserve maidency (reserve currency).
The backup currency is a currency that has a guarantee to a greater extent for international calculations or the formation of monetary reserves. Country-issuer reserve currency is permissible to pay debts before other states not gold, but by its currency. Reserve currencies in this period were recognized pound sterling and dollar. After the British Empire broke out (the British Commonwealth of Nations was issued by Westminster status in 1931) the role of the reserve currency was entrenched for the dollar. As a result, large financial crisis 1929-1933 The gold standard was distinguished in all states. In the domestic markets there was a refusal of all forms of payments in gold, there was a damage between the size of the gold reserves of banks and the volume of monetary emissions.
In 1944, there was a charter of the International Monetary Fund and established a fixed value of gold - $ 35 per Groin ounce (31.1 g). So the gold frame standard was installed. The world was formed by the Bretton Woods Monetary System, which was legally framed in 1944 at the UN Monetary Conference in Bretton Woods (USA). The main features of the currency system provided came to the following:
gold performs the functions of the personification of property and the means of international payments;
the payment fund function is also strengthened for reserve currency - US dollar:
the backup currency can be exchanged for gold;
comparison of currencies and their mutual exchange were performed on the basis of cash parities officially agreed by Member States, which were in gold and in US dollars. Parlyts were stable;
market currency rates had the opportunity to deviate from fixed dollar parities no more than 1%. 6.
Cancel fixed gold parities currencies and the transition to floating cash courses has become the last break step currency systems and gold. The Yamaican International Conference, the agreements of which were introduced in 1976-1978, legally fixed the motion of gold, which found a subsequent subsequent:
Official (fixed) value of gold is canceled;
Canceled the gold content of monetary units of states;
Gold is excluded from the calculations between the International Monetary Fund and its members.
Due to the fact that there was a deleting of gold, configurations in the structure of gold reserves were occurring. Stocks of IMF member states consist of 4 components:
1. Foreign currency - the means of other states belonging to the country provided: deposits in foreign banks, investments in securities that appeal on the international stock market, debt promises. The insignificate part of the component provided is represented by cash currency.
2. The backup point of view in the International Monetary Fund - the limit, within which the state automatically acquires from the Foundation the necessary foreign currency from the Foundation. The size of the limit corresponds to the amount of deposits of the provided state in the fixed capital of the Foundation in the form of gold and / or a freely convertible currency (25% of the total deposit amount).
3. SDR (calculated UNF unit), which the state has the right to apply to acquire other currency or for settlements with other Member States of the IMF.
4. The official state reserve of gold has the role of a reserve, which in the shortest possible time can be implemented and transformed into money. The share of gold in government reserves has decreased from 96% in 1938 to 20% in 1995.
Currently, in the bulk of states there is a transition to electronic and paper monetary systems. Distinctive features of such systems are as follows:
issuance of money for bank lending to the economic entities and under the increase of official gold wanders;
the formation of cashless currency turnover and the restriction of cash;
monopolization of cash emissions by the state represented by the issue bank;
dominant formation in the system of cashless currency turnover of electronic currency payments:
on the basis of universal prepaid cards (SARD-BASED SYSTEMS) - made on cards with stored cost, or on "electronic wallet";
on the basis of "Network Money" (SYSTEMS SYSTEMS) - the cash price is saved in the memory of computers, and with the help of a special software supply, it is fulfilled by its translation according to electronic communication grids (electronic payment systems of emission banks, Internet payments) ;
increasing the role of state regulation of currency circulation 8.
Centralized management of the National Monetary System;
Security of monetary signs manufactured in turnover, assets of the emission bank;
Forecast monetary turnover planning;
Elasticity and sustainability of money circulation;
Credit nature of monetary emission;
Provision only in lending to the government of funds;
Independence of the emission bank from the government and its accountability to parliament;
Comprehensive application of monetary regulatory tools 9.
Elements of national monetary systems are formed on the basis of these principles. The emission bank of the country producing cash is being implemented by the offer of money in the economy, and besides this and "creating" commercial banks. The amount of money supply depends on the main priorities of economic policies.
In the overwhelming majority of countries, currently there are monetary systems based on the circulation of undeveloped paper money, which is explained by their convenience, efficiency and elasticity. The principles of fiduciary monetary systems also apply to regional and international monetary systems.
Monetary system of industrialized countries. Modern monetary system includes the following elements - a monetary unit - the scale of prices - types of money - the emission system - the state or credit apparatus.
To describe the monetary system of industrialized countries, characterize it composite elements. The monetary unit is a monetary sign established by law, which serves to compile and express the prices of all goods. The monetary unit is divided into smaller multiple parts. In most countries, a decimal division system is 110100 1 US dollar equal to 100 cents.
Price scale means of expressing cost in monetary units, technical function of money. The official scale of prices has lost economic meaning with the termination of the exchange of credit money for gold. As a result of the Jamaician currency reform 1976-1978. The official price of gold and the gold content of monetary units canceled. Currently, the scale of prices is spoken by spontaneously and serves to compose the cost of goods through the price. The types of money that are a legitimate payment means are mostly credit banking tickets, as well as paper money Treasury tickets and a translating coin.
Banknotes Banknotes Type of money marks, legal payment ToolReceived by central banks. Banknotes are issued strictly defined dignity in the United States, banknotes are treated at $ 1,2,5,10,20,100 in the UK - at 1.5.10.20 pounds. Treasury tickets - paper money produced directly by the state to cover the budget deficit.
Unlike banking tickets, treasury tickets were never provided precious metals And they were not exchanged for gold or silver. After canceling the Golden Standard, the difference between treasury tickets and banknotes almost erased. Changing coin - metal ingot having established by law Weight content and shape. In the USA in circulation there are silver-copper and copper-nickel coins of $ 1,50,25,10.1 cent. In the UK, there are coins in 1 pound sterling, 50,10,5.2 pence, 1 and penny.
Have a walking of old coins in 2 and 1 shilling, which in terms of costs comply with 10 and 5 pens. The emission system in industrialized countries means issuing banking tickets by central banks, and treasury tickets and coins of treasury in accordance with the legislatively established issuing law. The emission of banking tickets is carried out by the issuing bank of the country in the process of lending to commercial banks, in the process of operations related to the purchase foreign currency and government securities.
In economically developed countries money turnover More than 95 is carried out in the form of non-cash payments. Therefore, an increase in the money supply in circulation occurs mainly no longer due to the emission of banknotes, but due to the deposit and check emission, i.e. In the process of lending by the emission bank of commercial banks. Monetary regulation is a complex of state impact measures to achieve compliance of the amount of money with objective needs of economic development.
In many industrialized countries since the 70s, targeting was introduced, i.e. The establishment of target references to the regulation of the growth of money supply in circulation, which are adhere to central banks in their policies. In this way, characteristic features Modern monetary systems of industrialized countries are the abolition of official gold content and free exchange of banknotes on gold, i.e. Demaneurization of gold - the transition to non-remitant on gold credit money - the issue of banknotes not only in the procedure of bank lending to the economy, but also to a large extent to cover the state's costs - the prevalence in the cash circulation of non-cash turnover is to strengthen the state regulation of money circulation. 1.3 State and Prospects for the Development of the Monetary System in the Russian Federation and the State Regulation The legal framework for the functioning of the monetary system in Russia is determined by the Federal Law on the Central Bank of the Russian Federation by the Bank of Russia of July 10, 2002. 86-F3 - the official monetary unit in our country is the ruble - The ratio between the ruble and the golden law is not established, and the ruble rate to foreign monetary units The Central Bank of the Russian Federation is determined by the exclusive right of cash issuance, the organization of their appeal and withdrawal in the Russian Federation has a bank of Russia, it is responsible for the state of money circulation in order to maintain normal economic activity In the country - types of money that has legal payment strength are banknotes and metal coins, which are provided by all the assets of the Bank of Russia, including the gold reserve, government securities, and reserves of credit institutions that are in the accounts of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation - Samples of banknotes and coins are approved by the Bank Russia - in Russia there are cash and cashless money.
In order to organize cash circulation on the territory of the Russian Federation, the Bank of Russia entrusted the following obligations - forecasting and organization of production, transportation and storage of banknotes and coins, as well as the creation of their reserve funds - the establishment of the rules of storage, transportation and collection of cash for credit institutions - the establishment of signs The solvency of monetary signs and the procedure for replacing damaged banknotes and coins, as well as their destruction - determination of the procedure for conducting cash transactions.
Since June 1997, the Bank of Russia has introduced the Regulation on the procedure for maintaining cash transactions in credit institutions in the Russian Federation of March 25, 1997. Regulation of the monetary circulation, held to the Bank of Russia, is carried out by using the interest rates in the market economy in the market economy loans to commercial banks, reserve requirements and operations in the open market.
For emission-cash regulation, cash service credit institutions and enterprises in the main territorial departments of the Central Bank, settlement and cash centers have revolving cash regulations on receiving and issuing cash and cash and reserve funds Cash tickets and coins.
Reserve funds of cash tickets and coins are reserves not issued in circulation of cash tickets and coins in the storage facilities of the Central Bank.
These funds are created by order of the central bank, which establishes their value based on the size of the current cash register, the volume of cash turnover, storage conditions.
In commercial banks, the creation of such funds is not provided, because They have operating cash desks.
Since June 1997, commercial banks have been established a limit of the minimum permissible cash balance in the operating office at the end of the day to ensure timely issuance of money from accounts legal entities, as well as with accounts on the contributions of citizens. The Central Bank of the Russian Federation recalculated ruble banknotes, in circulation as of July 1, 2002. The share of 1000-ruble bills is equal to 22, 500-ruble 54, the advantage of 100 rubles - 18.5, 50 rubles 4.5, 5 and 10 rubles -1 . The Central Bank of the Russian Federation informed about the increase by 9.3 money masses in Russia in the first six months of the current year to 1.75 trillion. rub. In this case, the increase in non-cash funds amounted to 8.5 to 1.11 trillion. Rub cash 10.5 to 0.64 trillion. RUB 2. Credit system 2.1.
End of work -
This topic belongs to the section:
Monetary system and its regulation by the state
Regulation of the monetary system by the state. 4. Problems of the formation of a credit system in Russia223. Conclusion25ii. Test27SPs .. The domestic credit and money system is not lucky. For regret, during .. speaking about this topic, it is impossible not to mention the problems faced by our economy in the transitional period ..
If you need additional material on this topic, or you did not find what they were looking for, we recommend using searching for our work base:
What we will do with the material obtained:
If this material turned out to be useful for you, you can save it to your social networking page: