Natural objects objects of artificial origin. Land plots by category
<*> Boltanova E.S. Natural Objects: Fiction In Law.Boltanova E.S., Associate Professor FGBOU VPO "National Research Tomsk State University", Candidate of Law, Associate Professor.
This article analyzes the current legislation, which uses legal fiction, proclaimed by the natural objects of those that are not. It is proposed to classify natural objects to natural and quasi-sided. Such a classification has not only theoretical value, but also a practical basis.
Keywords: natural object, quasi-rod, reservoir, artificial land.
In The Present Article The Modern Legislation, Which IS Used by Legal Fiction, Are The Natural Objects of Those That Are Not. It is offered to classify Natural Objects on Actually Natural and Quasinatural. Such Classification Has Not Only Theoretical Value, But Also The Practical Basis.
Key Words: Natural Object, Quasinatural Object, Reservoir, Artificial Land Lot.
In the dictionary of S.I. Ozhegova under the fiction is understood as "intentionally created position, construction, which does not correspond to reality, commonly used with any purpose"<1>. "The use of fictions in various fields of science is due to the fact that the use of this reception gives significant benefits, eliminating the need to provide unnecessary explanations about certain objects, phenomena ..."<2>.
<1> Ozhegov S.I. Dictionary of the Russian language / Ed. N.Yu. Swedio. M., 1998. P. 696.
<2> Jazoyan E.A. Category of fiction in civil law: dis. ... Cand. jurid science M., 2006. P. 4.
Fiction as a special reception of normation is known to Roman law. In a modern period, legal fiction is most often considered as a certain legal application that ensures the legal regulation of the relevant relations. As writes k.I. Slotsky, "Fiction ... is one of the recognized and effective legal techniques, and therefore the desire to get rid of the fiction is no more meaningful than attempts to avoid effective legal regulation of newly emerging relations ..."<3>. The use of legal ficiations brings stability to legal regulation.
ConsultantPlus: Note.
Monograph K.I. Skolovsky "Property in civil law" included in the information bank in accordance with the publication - the Statute, 2010 (5th edition, recycled).
<3> Skolovsky k.I. Property in civil law: studies. benefit. 3rd ed. M.: Case, 2002. P. 183. It is worth noting that there is a position that the fiction is "this is not the technical technique itself, but the result of technical activities." See: Dushakova L.A. Legal fiction: dis. ... Cand. jurid science Rostov-on-Don, 2004. P. 100.
One of the recognized species of ficiation is the fiction of artificially likenment and equalization (distribution of the legal regime)<4>. Researchers argue that equating (distribution of legal regime) is a historically the most progressive type of fiction, most frequently used in the modern legislation of all developed law enforcement<5>.
<4> See, For example: Dushakova L.A. Decree. cit. P. 85; Jazoyan E.A. Decree. cit. P. 11, 59, 127 - 142.
<5> See: Jazian E.A. Decree. cit. P. 11.
It seems that this species Legal fiction is used by the legislator when proclaiming the natural objects of those that are not.
Despite the fairly widespread use in the legislation of the term "Natural Object", its concept is contained only in the federal law "On Environmental Protection"<6>that, of course, emphasizes its ecological coloring and significance. In the context of the named law, the natural object is considered as part of the surrounding (including the natural) environment and is defined as "a natural ecological system, a natural landscape<7> and the components of their elements that preserved their natural properties ". Along with the natural object, natural-anthropogenic and anthropogenic objects are mentioned in the law. At the same time," the natural-anthropogenic object is a natural object, amended as a result of economic and other activities, and (or) an object, created by a person who has the properties of a natural object and having a recreational and protective value "; A" An anthropogenic object - an object created by a person to ensure its social needs and not possessing the properties of natural objects "(Article 1). Based on the provisions given, it follows that The natural object is distinguished from other types of objects inherent natural properties and the naturalness of its origin. And the term "natural" himself is interpreted in Russian as "natural"<8>. The naturalness of origin means that the natural object is an object to which human labor is not attached.<9>.
<6> See: Federal Law of January 10, 2002 N 7-FZ "On Environmental Protection" // SZ RF. 2002. N 2. Art. 133.
<7> The natural landscape is a territory that has not been changed as a result of economic and other activities and is characterized by a combination of certain types of terrain, soils, vegetation formed in unified climatic conditions.
<8> See: Large Explanatory Dictionary of the Russian Language / Ch. ed. S.A. Kuznetsov. SPb.: Norint, 2001. P. 988.
<9> The work as a conscious, targeted human activity covers all the forms of the active and conscious impact of a person on the environment.
This approach to the natural object finds confirmation and legal literature. So, A.K. Golichenkov emphasizes that "natural objects distinguish the following signs: natural (not as a result of human labor) the nature of origin, finding in a natural state ..."<10>. OL Dubovik notes that "the defining characteristic of this concept is their property, as the naturalness, the" naturalness "of the state, i.e. the invariance of human activity, although in relation to landscapes (even with a reservation - natural) this property is not always inherent in them"<11>. The norms of the Federal Law "On the State Real Estate Cadastre"<12> (hereinafter - the FZ about the cadastre) contrast the natural objects and objects of artificial origin (see: Art. 38, 39).
ConsultantPlus: Note.
Tutorial "Environmental Law of Russia: Dictionary of Legal Terms" A.K. Golichenkova is included in the information bank according to publication - Gorodets, 2008.
<10> Golichenkov AK Ecological law of Russia: a dictionary of legal terms: studies. Handbook for universities. 2nd ed., Pererab. and add. M.: Embed. House "Gorodets", 2012. P. 309.
<11> Commentary on the federal law of January 10, 2002 N 7-FZ "On Environmental Protection" (Pasteling) / OT. ed. OL Dubovik // prepared for the system "ConsultantPlus", 2010.
<12> See: Federal Law of July 24, 2007 N 221-FZ "On State Real Estate Cadastre" // SZ RF. 2007. N 31. Art. 4017.
If we turn to the standards of special legislation, they will find that the land (Article 1, 6 of the Land Code of the Russian Federation as natural objects are directly called<13>; Next - RF RF), forests, water bodies (part 2 of Art. 7 FZ about cadastre), water bioresources (Art. 1 of the Federal Law "On Fisheries and Conservation of Water Biological Resources"<14>). Legal literature is recognized that there are natural objects such as land, water, forests, subsoil, atmospheric air and an animal world, which corresponds to natural science offenses<15>. This approach to the types of natural objects as individual elements of environmental systems can be found quite narrow, but it is justified from the position of the existence of special legal regulation of their use and the protection of individual regulatory legal acts (land, water, forest codes, law on subsoil, etc.) .
<13> See: Land Code of the Russian Federation of October 25, 2001 N 136-FZ // SZ RF. 2001. N 44. Art. 4147.
<14> See: Federal Law of December 20, 2004 N 166-FZ "On Fisheries and Conservation of Water Biological Resources" // SZ RF. 2004. N 52 (Part 1). Art. 5270.
<15> See, eg: Volkov S.A. Nature management. Terminological directory. M.: GEOINFORMAMARK LLC, 2006. P. 387.
Currently, the expansion of a person in nature reached such sizes, which is less and less remains really natural, intact objects. In the place of the drained marshes appear pasture meadows, on the site of conceded trees - artificial forest stations, and the like. Considering the system of natural objects, in this article I would like to determine the place of objects possessing legal regime Natural objects, but not those due to the artificiality of their origin. This group includes some types of surface water bodies and artificial land. These objects are characterized by the fact that, as a result of their creation, one natural object (water object or land, land plot) disappears and another natural object appears in its place.
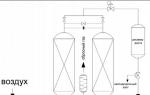
In the water code of the Russian Federation<16> (hereinafter referred to as VK of the Russian Federation) The ancient object is defined as natural or artificial water, watercourses, or a different object, permanent or temporary concentration of water in which has characteristic forms and signs of water regime. From the surface water objects listed in the Water Code, artificial origins, reservoirs, ponds, waterproof careers have. Only in relation to the legal nature of the channels, the legislator spoke quite definitely, by the type of hydrotechnical structure (Art. 3 of the Federal Law "On Safety of Hydrauthechnical Facilities")<17>. Channels are created in the process of hydraulic construction associated with the construction of structures and systems for water transport, land reclamation, water supply, sewage, etc.
<16> See: Water Code of the Russian Federation of June 3, 2006 N 74-FZ // SZ RF. 2006. N 23. Art. 2381.
<17> See: Federal Law of July 21, 1997 N 117-FZ "On the safety of hydraulic structures" // SZ RF. 1997. N 30. Art. 3589.
Reservoirs are artificial reservoirs created for accumulation and subsequent use of water and flow control. Ponds call reservoirs less than 1 square meter. km. Distinguish digging water bodies (ponds-kopani) or created by the permanent or temporary vehicle watercourse<18>.
<18> See: Reims N.F. Nature management. Dictionary-directory. M.: Thought, 1990. P. 422; Savtsk TM General landography: textbook for stud. institutions are high. Ped. prof. Education. 5th ed., Act. and add. M.: Academy, 2011. P. 230 - 232. The above provisions are fixed in GOST 19179-73 "Sushi hydrology. Terms and definitions".
Order of the Ministry of Environment of Russia dated January 26, 2011 N 17 "On approval of guidelines for the development of rules for the use of reservoirs" Among the types of reservoirs on geometric sizes are highlighted with small reservoirs (less than 2 square meters. Km).
The current legislation declares that the reservoir is a surface water object (art. 5 of the Russian Federation of the Russian Federation). As you know, dams, hydraulic structures designed to protect against the destruction of the shores and the bottom of the reservoirs, and the associated objects (pumping stations, water intakes, gateways, hydroelectric power plants, water intakes, gateways, hydroelectric power plants, etc.). Each of these structures necessary for the appearance of the reservoir and its generators or for the use of water resources contained in the reservoir is an independent object of rights, most often - the object real Estate. Such independence is relative. Without the construction of water damping facilities, the emergence and existence of reservoirs is impossible, but also without a water facility, the structures will not fulfill its purpose and function. The construction of objects forming the reservoir occurs in the process construction work, and their nature as hydraulic structures (facilities intended for the use of water resources and preventing the negative impact of water) is no doubt. Attention is drawn to the fact that the process of creating a reservoir is nothing more than the construction of this object as a whole. During the construction of the reservoir, project documentation for the reservoir (and not only for the formed hydraulic structure) is being developed and measures are being carried out in relation to the reservoir territory as a whole (for example, sanitary preparation of the territory of flooding), an acceptance of a reservoir is carried out into operation by the State Commission.
In accordance with the water legislation, the reservoir (covered with waters, the so-called flooding zone, together with its components, and its shores) is an aqueous object, although in general the reservoir is a unique man-made object as a result of construction activities. The reservoir is a interconnected and interdependent system of a converted water object (for example, rivers, lakes, on the place of which the reservoir is created) and the land surface (the lodge of the reservoir), as well as hydrotechnical (s) structures (s).
Public relations on the creation of ponds and flooded quarries, unlike reservoirs, remained outside the zone of attention of the legislator. Much of the above applies to the characteristic of the pond as a variety of reservoirs. When creating a pond-kopani, a significant change in the land surface occurs, as a result of which this surface is legally considered as a composite, not an independent part of the water object - the pond. By the way, in law enforcement practice, you can meet evidence that the ponds are permissible to qualify and as structures<19>.
<19> See, for example: Resolution of the FAS of the Volga-Vyatka District of September 27, 2007 in case No. A38-2776-17 / 539-2004 // ATP "ConsultantPlus: Departure Printing".
Careers are formed as a result of mining open way and are cavities in the earth's crust<20>. Flooded careers are not specially created objects, but a consequence of termination of work on mining and artificial or naturally filling in water formed recesses. Mining of minerals and filling with water formed generation indicate a change in the legal status of not only the land surface, but also a plot of subsoil (underground space).
<20> See: Hydroecology and environmental management. The conceptual-terminological dictionary / authors-compilers V.V. Kozin, V.A. Petrovsky. Smolensk: Okuman, 2005. P. 160.
Water objects can be used to create artificial land plots <21> (p. 19 h. 3 of Art. 11 VC of the Russian Federation). The water code is limited only by reference to the possibility of creating such sites. Separate norms about artificial land plots could be found in the Federal Law "On Maritime Ports in the Russian Federation and on Amendments to Selected Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation"<22>, regional legislation. Letter of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation of March 31, 2009 N D23-836<23> It was emphasized that "the legislation shares cases of creating artificial land plots when the waterflines of the Water Foundation are rented or sucking the ground (not having independent meanings), as a result of which they acquire the sustainable properties of the land plot, and cases of creating hydrotechnical structures created by On the lands of the water fund by renovate or swelling the soil, having an independent value (dams, dams, etc.). " In fact, the question of ownership of the newly created object was resolved in the mentioned letter. The absence of clear criteria for the distinction of artificial land and hydraulic structures has already been indicated in legal literature<24>.
<21> The world has the construction of artificial land plots in order to increase the area of \u200b\u200bresidence of citizens, especially in countries experiencing difficulties with land territory. Washing areas are widespread in Japan, the Netherlands. Perhaps the most famous example is the project "Palm Jumeirah" (Dubai), which began in 2001, - the creation of an artificial island in the waters of the Persian bay with a total area of \u200b\u200b25 square meters. Since 2012 in Sochi, it was planned to begin construction in the water area of \u200b\u200bthe Black Sea of \u200b\u200bthe Washing Island "Federation" of more than 250 hectares (the official website of the project: www.federationisland.ru).
In other Russian cities, work is also underway in this direction. In particular, in St. Petersburg, a project "New Beach" was developed, providing for the creation of 390 hectares by naming an artificial territory with an area of \u200b\u200b390 hectares, by 2028 - it is planned to complete the construction of real estate objects in this area. In Vladivostok, there is a refreshing project about 3 hectares of territory to use it under the embankment and other public destinies.
<22> See: Federal Law of November 8, 2007 N 261-FZ "On Marine Ports in the Russian Federation and on Amendments to Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation" // SZ RF. 2007. N 46. Art. 5557.
<23> See: Letter from the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation of March 31, 2009 N D23-836 // ATP "ConsultantPlus".
<24> See, eg: Melnikov N.N. Artificial land plot: search for universal definition // Journal of Russian law. 2011. N 5. P. 24 - 30.
With the adoption of the Federal Law "On artificial land plots created on water bodies in federal property, and on amending the individual legislative acts of the Russian Federation"<25> (hereinafter - the Federal Law on Artificial Lands) in russian legislation The concept of an artificial land plot created on a water facility in federal property, created in a federal property being created in a federal property, or part of the soil, or the use of other technologies or the use of other technologies was obtained. Artificially created land plot can fit to existing land or be isolated from them (Article 3 of the Law).
<25> See: Federal Law of July 19, 2011 N 246-FZ "On artificial land plots, created on water bodies in federal property, and on amending certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation" // SZ RF. 2011. N 30 (Part 1). Art. 4594.
Entering an artificially created land plot entails the transformation of the object of federal ownership of the water object (reducing the water area, changing its area, borders, configurations) and is recognized as a legal fact with which the law binds the emergence (including the moment of occurrence) of ownership of artificial land Plot (Article 13 of the FZ on artificial land). Artificial land plot can be in all declared by the federal law of property forms.
You can agree with those authors who believe that "from a technological point of view, the process of creating an artificial land plot should be considered construction"<26>. Indeed, as a result of consistently implemented actions that characterize the construction process (survey work, the preparation of the construction site, construction and installation work, etc.), an object that is firmly associated with the Earth (natural surface) appears. Although I note that, taking into account the climatic conditions, the hydroresum of the water object and other factors, the construction of an artificial land plot is associated with the device of the beverage, including the hydrotechnical, structures. Not by chance and art. 4 Town Planning Code of the Russian Federation<27> enshrines that the relationship associated with the creation of artificial land plots is applied town planning Taking into account the features established by the Federal Law "On artificial land plots created in water bodies in federal property and on amending the individual legislation of the Russian Federation."
<26> Kirillov A.A. Legal regime of artificial land // Lawyer. 2011. N 18. P. 15.
<27> See: Urban-Planting Code of the Russian Federation of May 7, 1998 N 73-FZ // SZ RF. 1998. N 19. Art. 2069. Entry.
After entering the structure (artificial land plot), it is also recognized as a land plot, and the legal regime of the land plot is distributed. The double status of an artificial land plot as a created structure and a land plot The legislator emphasizes using two terms in the Federal Law of Artificial Lands: "Operation" and "Use" (Article 12, 15). The operation of artificially created land plots is carried out in accordance with the legislation on urban planning activities, and its use and turnover is in accordance with the Federal Law on Artificial Land, civil law and land legislation.
Artificial land plot represents a certain boundaries, a technogenic surface, isolated from soils<28> On the natural basis. Like an artificial water object, the properties of the natural system, an artificial land plot not immediately. After its creation, the process of sealing and self-removal of the soil continues, hardening by forming structural links (clutch), the process of soil formation is possible, when used (albeit limited) artificial sites for recreational, agricultural purposes.
<28> In the science of land, as opposed to natural soils, such a concept as "urbotechnozhe", to which they include varieties of urban soils, created often on displaced bulk or woven soils (see: Sladkopevtsev S.A. Region and environmental management: student learners. Handbook for university students . M.: Higher. Shk., 2005. P. 313).
The water code mentions artificial islands and artificial land plots, without distinguishing them. The creation of artificial islands is often due to the exploration and mining of mineral resources. for example, in accordance with paragraph 6 of Art. 16 of the Federal Law "On Internal Sea Waters, the Territorial Sea and the adjacent zone of the Russian Federation"<29> With regional geological study, geological study, exploration and mining of mineral resources in inner sea waters, in the territorial sea, the license for the use of subsoil provides its owner the right to create, exploitation, the use of artificial islands. On the continental shelf, the creation, operation, the use of artificial islands can be carried out for regional geological study, geological study, exploration and mining of mineral resources (Article 16, 16.1 of the Federal Law "On the Continental Shelf of the Russian Federation"<30>). The construction of stationary and (or) floating platforms, artificial islands on the lands coated with surface waters, is carried out on the basis of decisions on the provision of water bodies to use (paragraph 4 of Part 2 of Art. 11 of the Russian Federation), whereas for artificial land plots of such a decision No required (p. 19 h. 3 of Art. 11 VC of the Russian Federation). It can be assumed that the artificial island is not a type of artificial land, which is isolated from other land plots with water, and a special type of real estate, which is created as a structure and is further considered by the legislator exclusively as a structure (and not a land plot, natural object). So, according to Art. The 20 federal law "On the Continental Shelf of the Russian Federation" in order to ensure the safety of shipping, abandoned or no longer used artificial islands should be removed by their creators within the deadlines specified in the resolution of their creation.
<29> See: Federal Law of July 31, 1998 N 155-FZ "On internal sea waters, territorial seas and adjacent zone of the Russian Federation" // SZ RF. 1998. N 31. Art. 3833.
<30> See: Federal Law of November 30, 1995 N 187-FZ "On the Continental Shelf of the Russian Federation" // SZ RF. 1995. N 49. Art. 4694.
Thus, in the considered cases, we can observe the appearance of objects artificially created as a result of targeted human activity, which in the initial state may not even have natural properties. In any case, such objects do not have natural origin. Strictly speaking, on the basis of the content of the norms of the Federal Law "On Environmental Protection", it cannot be said that artificial reservoirs and artificial land plots are natural and anthropogenic objects.
The legal definition of a natural anthropogenic object indicates its two types: an initial natural object and an object (not natural), which is changed as a result of human activity (not natural) with natural properties. As can be seen from the above, there is a transformation of an initially existing natural object to such an extent that the newly created object "flashes" by itself natural resourceFrom which it was formed, and acquires an independent, autonomous "life", value and legal regime. Yes, and defined in Art. 1 of the Federal Law "On Environmental Protection" The importance of a natural-anthropogenic object - recreational or protective is for an artificial water object and an artificial land plot far from decisive and the only one.
for exampleIn accordance with the FZ on artificial land plots, artificial territories are created in order to build buildings, structures and (or) of their integrated development for construction purposes.
Earth, subsoran at the site of the reservoir formation (including a pond), a water-watering career, channels are modified and become only part of Surface water object<31>; An aqueous object in a separate part in the construction of an artificial land plot is converted into a land-ground surface. From a legal point of view, it is important to change the priority of applied regulatory legal acts governing the use of these objects. The newly formed objects are referred to as a legislator with natural in order to spread the legal regime of the natural object.
<31> By virtue of Art. 5 Water Code of the Russian Federation Surface water objects consist of surface waters and lands coated within the coastline.
There is a use in Russian legislation regulating the use and protection of land, water bodies, legal fiction.
Thus, revealing the system of natural objects, it is possible to discharge in their composition along with the natural objects of a separate subgroup and the designation of their quasi-solid objects, "as if natural objects". Such objects, although they are recognized as natural, do not have natural origin and often have double status. The use of the quasi console allows you to pay attention to the special nature of the appearance of such objects, in some cases - to the specifics of their operation. Each of the quasi-elephant objects is an artificially created system with the metabolism and energy between the alive and non-resident elements established for a certain time. The environmental system formed under the influence of natural factors usually requires maintenance from human (filling and workout (water output) reservoirs, the production of bererectic works, etc.). The quasi-rod object is covered by the legal regime of the natural object and the container of the components of the natural environment, as well as a man-made (artificial) object. Accordingly, the legal regulation of public relations on these objects is based on a significant number of standards aimed at their protection, special standards for their use, on the one hand, and regulatory rules for their operation<32>On the other hand, having different content and nature.
<32> The exception, perhaps, constitutes waterproof careers, is based on the appearance of which there are no activities aimed at creating such special objects, their use may not be submitted to the rules of operation. Operation of objects implies monitoring their condition, performing repair work to eliminate damage, design deficiencies and similar work.
The classification of real estate objects on various features (criteria) contributes to a more successful study of objects. For these purposes, you can apply different principles of classification depending on their origin and destination. However, the definition of real estate involves the allocation in its structure of the two components (Fig. 1.1):
Fig. 1.1. Enlarged classification of real estate objects
1. Natural (natural) objects - Plot, forest and perennial plantings, separate water bodies and plots of subsoil. These real estate objects are also called "real estate by nature".
2. Artificial facilities (buildings):
but) residential Properties - Low-storey house (up to three floors), multi-storey house (from 4 to 9 floors), house enhanced floor (from 10 to 20 floors), high-rise house (over 20 floors). The object of residential real estate can also be a condominium, section (entrance), floor in the stairwell, apartment, room, country house;
b) commercial real estate - offices, restaurants, shops, hotels, garages for rent, warehouses, buildings and structures, enterprises as a property complex;
in) public (special) buildings and structures.
-
Medical and wellness (hospitals, clinics, nursing homes and houses of a child, sanatoriums, sports complexes, etc.);
- educational and educational (kindergartens and nursery, schools, colleges, technical schools, institutes, children's creativity houses, etc.);
- Cultural and educational (museums, exhibition complexes, parks of culture and recreation, houses of culture and theaters, circus, planetarium, zoos, botanical gardens, etc.);
- Special buildings and structures - administrative (militia, court, prosecutor's office, authorities), monuments, memorial structures, train stations, ports, etc.;
d) engineering facilities
- Meliorative structures and drainage, integrated engineering preparation of the land plot for development, etc.
Each of these groups can be further disaggregated on the basis of various typological criteria.
Artificial facilities were called - "Real Estate by Law", but this real estate category relies on "real estate by nature".
Artificial objects can be fully built and ready to operate, may require reconstruction or overhaul, and also relates to Unfinished construction facilities (incomplete). According to Soyugetrostroy, there are about 1,500 houses and, according to experts, about 500 industrial and civilian facilities are located at work of unfinished construction. To "incomplete" refer objects for which in the prescribed manner are not issued by the acceptance of an object of operation.Objects of unfinished construction can be divided into two groups: objects on which work are underway, and objects for one or another reasons are discontinued. In accordance with the current procedure, there are two types of termination of work at the facility: preservation and complete cessation of construction. Decision on termination of construction takes an developer. The solution should indicate the reasons for conservation or complete cessation of construction, as well as:
- at preservation - the term for which is preserved (temporarily stopped) construction, conservation conditions, the name of the organization on which the construction preparation is assigned to conservation, the safety of constructed objects and work performed;
- With full termination of construction - the procedure for the elimination and use of already constructed objects or their parts, mounted structures and equipment, the realization of material values \u200b\u200bdelivered to the construction site.
Currently, in St. Petersburg, there is a procedure for the preparation and issuance of a passport of the object of unfinished construction (adj. 3), which is a single document on the territory of St. Petersburg, which contains a description of the object of unfinished construction and includes an exhaustive object of information.
Land May be divisible and indivisible. The plot is called divisible when it can be divided into parts and to form independent land plots with the permission for the target use (adj. 4). In accordance with the legislation, the section of urban lands, land farms, etc.
The land fund in the Russian Federation for economic purpose is divided into seven categories of land:
1. Agricultural land Have a special legal status in the real estate market and are used:
- for agricultural production (pashnya, hayflowers, pastures, deposits, perennial plantings, virgin and other land);
- for personal subsidiary economy;
- for collective gardening and gardening;
- for utility agricultural production;
- For experienced and scientific stations.
Land translation from this category to another is carried out only by the decision of the subject of the Federation. Particularly valuable lands are not subject to privatization.
2. Lands of cities and settlements occupy 4% of the country's territory. These lands are located residential buildings and socio-cultural institutions, as well as streets, parks, squares, environmental structures; Industrial, transport, energy, defense facilities and agricultural production can be placed. This land category provides 86% of income into the consolidated budget from all payments for land use and can only be used in accordance with the general planners and projects.
3. Industry, transport, communications, television, computer science and space support, energy, defense and other purposes. Have a special use mode.
4. Lands of specially protected territories include reserves; Green cities, rest houses, turbases; Monuments of nature, history and culture; Mineral waters and medicinal dirt, botanical gardens, etc. This category of land is intended for the improvement of people, mass recreation and tourism, as well as for historical and cultural education and aesthetic pleasure. Such lands are protected by special legislation, and they are prohibited on them to lead economic activities.
5. Lands of the Forest Foundation are fully determined by the legal regime of forests growing on them. This category of land includes land covered with forests and provided for the needs of forestry and local industry.
6. Lands of the Water Fund. These are lands engaged in reservoirs, glaciers, swamps (except tundra and timber tundra), hydraulic structures and rope strips with them.
7. Earth stock serve as a reserve and stand out for various purposes.
The sale of land, as well as the allocation of them for entrepreneurship and transfer from one category to another, is carried out in accordance with the laws of the Russian Federation and the subjects of the Federation.
So, for example, a list of lands is defined in St. Petersburg target use that are not subject to sale. These include:
but) located in the state (municipal) property:
- protected or specially used natural areas (reserves, nature monuments, national and dendrological parks, botanical gardens, etc.);
- Land plots of the historical and cultural heritage of the federal importance on the list approved by the Government of the Russian Federation;
- Land plots of forest and water funds;
- land plots of recreational and historical and cultural purposes;
- Land plots of crematoriums and cemeteries;
b) unaked land plots:
- agricultural purposes, forest and water funds, especially protected land, for which the legislation of the Russian Federation has established a special privatization regime;
- infected with hazardous substances and subjected to biogenic infection;
- general use (streets, passages, roads, embankments, parks, forestarks, squares, gardens, boulevards, reservoirs, beaches and other sites related to the legislation to general use);
- located in marine, river and air ports of federal significance or allocated (reserved) for their prospective development;
- in temporary use without the right to build capital buildings;
- on which there are disputes on the accessories of these sites or firmly related real estate at the time of treatment;
- other not subject to privatization in accordance with the legislation.
The above lands are categories current use of the land plot those. not for sale.
The plot in the turn is used to obtain income, including by transferring to rent, introduction to share capital, to ensure pledge, etc.
The territory of St. Petersburg is divided into 19 zones, depending on its value. For each zone installed its tax rate (see Table 1.1).
Table 1.1.
Land tax rates on urban-planning values
|
Rate rub. / sq. m per year |
Rub. / Sq. m per year |
Rub. / Sq. m per year |
|||
Land tax pay:
- citizens and companies with plots in the property;
- enterprises and institutions, to which the land was transferred to permanent (permanent) use;
- Individuals whose stuff is fixed on the basis of lifetime inherited ownership.
The rate of bet does not depend on what business is the owner.
For those who breed a garden, engaged in agriculture or holds a garage, special rates are provided (see Table 1.2).
Table 1.2.
Tax rates set for individual land categories (per year)
|
Purpose of land |
Tax rate |
|
Earths employed under gardening, gardening, animal husbandry |
0.144 rubles / sq.m |
|
Earth agricultural use |
66,528 rubles / ha |
|
Earths located in the outlet strip |
|
|
Earth engaged housing Foundation |
3% of the rate provided for each zone of town planning value, but not less than 0.144 rubles / sq. M. |
|
Earth engaged in individual and cooperative garages |
3% of the bet, but not less 0.144 rubles / sq. M. |
IN private property There is 7301 hectares, which is 5% of the territory of the Big Petersburg. Citizens mostly own sites in individual residential buildings (1113 hectares). Enterprises occupy 5432 hectares, 4321 hectares are employed under agricultural lands.
The procedure for the sale and sale of land plots engaged in privatized state (municipal) enterprises is determined by the "main provisions of the State Program for the Privatization of State and Municipal Enterprises in the Russian Federation after July 1, 1994", approved by the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation from 22.Iulyu 2004 No. 1535, and Also near other regulatory acts.
The seller of the above-mentioned land plots is the fund of the property that has been selling a certain enterprise or shares joint Stock Companycreated during the privatization of the state (municipal) enterprise.
The object of sale is a plot involved in the building, construction, a premises, which is owned by the buyer of the land plot, and for enterprises - a plot within the territory of the land user.
Buyers of land under a privatized enterprise, building, construction, facilities can apply for the redemption of the land plot completely or partially.
Application is mandatory attached to the application. the following documents:
- for legal entities - a notarized copy of the constituent documents or their script;
- for individuals - a copy of the passport or document replacing it;
- contract of sale or other documents confirming the ownership of all buildings, structures located on the repurchased land plot;
- three copies of the project of the borders of the land plot issued by the Committee on Town Planning and Architecture (CGA);
- three copies of a land plan, issued and certified by the Committee on Land Resources and Land Management (KZRIS);
In the absence of the buyer of the documents listed above, the application is made by the decision of the authorities on the provision of land plot, which indicates the area and location of the site, as well as a copy of the privatization plan;
Extract from the register of shareholders (constituent contract) confirming that at least seventy percent of the authorized capital of a legal entity is in private ownership;
Help on the sources of funds sent to pay under the purchase and sale agreement (for legal entities), or a certificate of income (for individuals) registered in the territorial tax authority.
The seller (property fund) after receipt of the application and documents is registered and sends requests to KZRIZ, KGA and the Committee on State Control, the Use and Protection of History and Cultural Monuments (Hiop) (if the inventive area is within the borders of the monument areas) on issuing conclusions on this land plot. In a month, these organizations issue a conclusion (on providing or providing land plot) and two copies of it.
The sale price of the plot in St. Petersburg is calculated as a product of the area of \u200b\u200bthe site, the regulatory price of the Earth and the increase in the coefficient established in accordance with the order of the mayor - Chairman of the Government of St. Petersburg dated August 22, 1994 No. 881-R "On the procedure for determining the price of the land plot" . The regulatory value of the plots is from 10 to 85 tax ratesDepending on where it is located, and who buys it.
When buying a land plot in parts as such a part there may be:
Land under geographically separed division or other part of the enterprise;
Land plot of an enterprise where one or more buildings, buildings, structures are located.
When selling a land plot It is important to understand that it is also necessary to identify the fate of other real estate related properties, because only the land plot is sold, only the ownership of land goes to the buyer, and the seller retains the rights to the buildings, structures and other Objects and the right to use the part of the land plot that is occupied by this object of real estate and is necessary for its use on the terms determined by the Treaty of Sales.
At the local level, in particular, in St. Petersburg, land legislation in terms of the sale of land plots is currently represented by various subtitual acts and regulatory documents. First documentRelated directly to the sale of land in St. Petersburg, was the disposal of the mayor from 19.10.94. No. 1043-r "On the procedure for the implementation of the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of July 22, 1994 No. 1535 in terms of sales and rental of land plots" . This disposal determined that the seller of land plots is the city property fund, the landlord - the Committee for the Management of Urban Property, and the Registrar (including the registration of land and other real estate themselves, the rights to the plots and the associated real estate, the description of the primary servitors, other burdensions and T .d.) - Kzriz St. Petersburg.
Registration and issuance of certificates of ownership and the right of life inherited ownership citizens primary decoration rights to land plots provided for individual housing, country construction, gardening and gardening;
registration and issuance of certificates of the right of indefinite (permanent) use to land legal entities; Registration and issuance of certificates of ownership of land to agricultural enterprises carry out crues. The procedure for admission, consideration and issuing documents in the primary design of certificates of rights to land plots is regulated by the instruction.
The procedure for the sale and sale of land plots in St. Petersburg suggests that a significant proportion of work on the privatization of the Earth is given to KZRIS.
In material assets of the commercial organization, sites are taken into account in its property, and in intangible - provided or acquired real and obligatory rights to them.
These rights in accordance with the current legislation applies to the right:
life inherited possession of state and municipal property sites;
permanent (perpetual) use of areas of state and municipal property;
lease of land;
Limited use by adjacent land plots owned by other persons.
In the course of operation, the land plot may bring income, called land rent. Under it it is understood as the internal indicator of the effectiveness of the use of the everch area as, an asset of an enterprise, which is calculated as the private from dividing the calculated value of the cost for the period of capitalization.
In accordance with the draft methodological recommendations "Procedure for accounting for the value of land plots in assets commercial organizations, including with foreign investments, "developed by the State Committee of the Russian Federation for land resources and land management, when calculating land rent next classification Land Depending on the type of use: agricultural, forestry, land of settlements, etc.
The above systems for the classification of fixed assets and land plots are currently accepted as a basis for accounting in the assets of enterprises. but they consider real estate objects not as a whole, but as basic funds and land. However, if analyzing precisely market value Real estate, there is a need to develop its own classification system, which would take into account the main "commodity" properties of a holistic assessment object and would be linked to already existing classification systems and object descriptions.
With regard to residential real estate objects, several typological constructions are possible. For example, depending on the duration and nature of the use of housing:
- primary accommodation - place of permanent residence;
- Secondary housing - Country housing used for a limited period of time;
- Tertiary housing - intended for short-term accommodation (hotels, motels, etc.).
In relation to the conditions of major cities (for example, St. Petersburg), it is customary to allocate the following typological characteristics:
1. Luxury housing.
The following basic requirements are presented to it:
§ accommodation in the most prestigious areas of the city;
Belonging to the "old" foundation (in the presence of a capital repairs and reconstruction) or to the "Stalinist" fund;
Brick walls;
The total area of \u200b\u200bapartments is at least 70 square meters. m.;
The presence of isolated configuration rooms approximate to the square, and a large kitchen (at least 15 sq.m.);
The presence of a protected entrance, an underground or nearly located garage, etc.
For low-rise cottage-type houses that are part of elite, characteristic of such consumer requirements, as:
§ accommodation at such a distance to the city when the trip takes no more than 1 h;
Brick walls;
Development in two or more levels;
The presence of household and engineering facilities.
2. Housing of high comfort.Consumer demand for housing this type involves the presence of the following basic characteristics:
The possibility of accommodating in various (not only the most prestigious) areas of the city;
Some reducing requirements for rooms and kitchens up to 12 and 8 square meters. m (respectively);
The presence of a living room with an area of \u200b\u200bat least 17 square meters. m.;
Large variety of structurally technological parameters.
Applied to low-rise houseslocated in the suburban zone, the main characteristics is high strength, durability and low thermal conductivity of walls, as well as security engineering networks.
3. Typical housing.It is characteristic of:
Accommodation in any area of \u200b\u200bthe city;
Compliance of architectural and planning parameters with modern construction standards and rules;
According to constructive technological parameters, belonging to the houses of the second generation of industrial house-building and modern.
For low-rise suburban construction, not only technical characteristics, but also the security of the main objects of socio-domestic destination are the most significant.
4. Housing of low consumer qualities
Based on the conditions of consumer demand formed under the influence of the solvency factor, the requirements for this type of housing are very small:
Accommodation in non-varying areas;
Distance from major transport communications;
Belonging to such constructive technological types as the buildings of the "old" fund, not subjected to capital and repair and construction work, and the house of the first generation of industrial home-building;
Accommodation in the first floors of other types of houses;
Understated architectural and planning characteristics, etc.
The considered classification takes into account the preferences of the target groups of housing consumers and the level of their solvency (marketing approach). However, residential real estate can be distributed on the basis of urban benchmarks.
So, when making economic decisions in the residential real estate market of St. Petersburg, typology is used, including:
Houses "Old" Foundation, built in the pre-revolutionary period;
Houses built for the period from 1917 to the late 30s, distinguished by laconicism of architectural and planning solutions located in close proximity to the place of application of labor (of the period), little more prestigious, but possessing high constructive and technological characteristics ;
The "Stalinist" houses, the term of the construction of which fell for the period from the end of the 30s to the end of the 50s, marked by the revival of classical architectural and town planning positions and located mainly in prestigious, distant from industrial areas;
Houses of the first generation of industrial home-building (60s) (Khrushchev), characterized by understated architectural and technological parameters;
Houses of the second generation of industrial house-building, built in the 70-80s, when higher norms and standards were used in urban planning;
Modern residential buildings, distinguished by a large variety of characteristics.
Table 1.3.
and the number of rooms in St. Petersburg
|
Qualitative "Old |
|||||||
|
Non-quality |
|||||||
|
"Old Fund" |
|||||||
|
Qualitative "Stalin- |
|||||||
|
sky House |
|||||||
|
Non-quality |
|||||||
|
"Stalin's House" |
|||||||
|
Brick "Khrushchevki" |
|||||||
|
Panel "Khrushchevki" |
|||||||
|
and "Brezhnevka" |
|||||||
|
"Ships" |
|||||||
|
Other panels |
|||||||
|
multi-story houses |
|||||||
|
Modern bricks |
|||||||
There is I. classification of residential real estate objects depending on the material of the exterior walls of the building:
- houses with brick walls;
-
panel houses;
- monolithic houses;
- wooden houses;
- Funny-type houses.
Separate niche occupy objects of suburban real estate due to a minor transaction volume and their specificity. Basically, secondary housing is presented here.
Many factors affect demand and supply in this market sector. In addition to ordinary priorities when buying residential real estate, personal interests are of great importance to location, the time of year, the social homogeneity of the neighbors. Buyers pay great attention to the presence of a complete range of communications (autonomous systems of heat and water supply). Preference is given to objects of brick or wood. As a mandatory attribute, a minimum of 10 acres is considered as a mandatory attribute to the suburban real estate.
The following areas include the greatest demand in the Leningrad region: Vsevolozhsky, Primorsky, Toksovo, Karelian, Yukki, etc.
The average prices in the country real estate market from 5 to 13 thousand CLUA, although elite cottages and winter houses are at a special account and are estimated from 50 to 100 thousand US dollars.
Signs of the classification of residential real estate that served as the basis for the grouping is different, as well as their motivation, preferences and solvency conditions. Use a single typological criterion that integrates the influence of all factors is not possible. Therefore, in practice there are several criteria that give a reasonable idea of \u200b\u200breal estate.
Commercial real estate In Russia, it became formed only with the beginning of the privatization of enterprises. The commercial real estate sector is much smaller than residential, therefore transactions, respectively, although worldwide commercial real estate is the most attractive. It should be noted that in this sector the prevailing form of transactions is rental.
Commercial real estate can be divided into revenue - actually commercial real estate and creating conditions for its extraction - industrial (industrial) real estate.
Real estate that makes income can be attributed:
1. Office space. When classifying office premises in each region, municipal Education Various factors are accepted by which the room refers to a particular class. It can be a location, quality of the building (finishing level, facade, central entrance condition, the presence of elevators), management quality (management company, the availability of additional services for tenants), etc.
International practice uses the following classification:
Class A1:
1. International developer.
2. Central location, convenient access.
3. Fully rebuilt building.
4. The microclimate is controlled by the help of a single ventilation system, heating and a four-pipe air conditioning system.
5. Open planning of space according to the Standard "Shell-and-Sog":
- false floors and suspended ceilings,
- Height from floor to the floor of the next floor 3.6 m,
- rational effective grid columns - the distance between them is at least 6 m.
6. Underground parking and convenient access.
7. Uninterruptible power supply system.
8. Modern systems Building security.
11. International Management Company.
Class A2:
2. Fully reconstructed in the 90s. building.
3. Fully controlled microclimate indoor.
4. Open planning of space according to the Standard "Shell-and-Sog".
5. Sufficient parking and easy access.
6. Uninterruptible power supply system.
7. Modern building security systems.
8. Professional landlord.
9. Properly executed documentation for the ownership of the building.
10. International Management Company.
Class B1:
1. Central location, convenient access.
2. Reconstructed building.
3. Autonomous heat supply and pre-cooling system of supply air.
4. Effective layout of floors in the form of office blocks.
5. High-quality repair "Eurostandard".
6. Sufficient parking and easy access.
7. Modern elevators.
8. 24-hour security.
9. Professional landlord.
10. Properly decorated documentation for the ownership of the building.
11. Professional management company.
Class B2:
2. Repaired building.
3. Effective layout of floors in the form of office blocks.
4. High-quality repair "Eurostandard".
5. Not very convenient access is possible.
6. 24-hour security.
7. Professional landlord.
8. Properly executed documentation for the ownership of the building.
9. Professional management company.
Class C1:
1. Central location.
2. Cosmetically renovated building.
3. Effective layout of floors.
4. Quality repairs.
5. 24-hour security.
6. Experienced landlord.
7. Properly decorated documentation for the ownership of the building.
8. The presence in the building of the control structure.
Class C2:
2. The project arose by converting the former institution or an administrative building.
3. Various state of premises: from the repair of Soviet type to the modern stylish interior.
4. 24-hour security.
5. Properly executed documentation for the ownership of the building.
6. The presence in the management structure in the building.
ClassD.:
1. Various location.
2. Not very convenient access.
3. The project arose by converting the former institution or an administrative building.
4. Cheap repair.
5. Protection.
6. Properly executed documentation for the ownership of the building.
7. Lack in the management structure building.
In various regions of Russia, this classification may not coincide. So, for example, in St. Petersburg, as a result of the study of existing office centers, the following classification was determined.
Class A:
-
central location;
- new construction or capital reconstruction;
- highly professional management;
- a wide range of services;
Class Q:
-
good location;
- separately worth the specialized office building;
- selective overhaul;
- professional management;
- a wide range of services;
- Full business security.
Class FROM:
- good location;
- detached building;
- redecorating;
- management;
- Services.
ClassD.:
-
Commercially, unconvened administrative and production and laboratory corps of medium and large enterprises.
Among the factors that affect the attractiveness of office centers created near industrial enterprises or on their territory (class D), you can allocate:
2. Hotels. Hotel projects today in the Russian Federation are the most complex types of investment in rectic real estate. Construction of new or reconstruction of old hot-class hotels, their equipment and operating costs are considered a fairly risky investment of money, because The costs of such projects are several times higher than the cost of building trendy shopping complexes or office centers. In addition, five-star hotels have a very long payback period, so the Russian revenue real estate market is a low tariff hotel and lower capital investments.
At the time of time hotel St. Petersburg is very divergent and includes more than 100 objects of various categories by 27 thousand seats. Most of these hotels are small. 30 hotels can be attributed to more or less noticeable, which accounts for 55% of the total number of hotel places in the city. Major hotels include: "Baltic", Pulkovskaya, Moscow, St. Petersburg. In St. Petersburg, there are not enough mid-level hotels. The five-star belongs: the Grand Hotel "Europe" and "Nevsky Palace". The return on investment in the construction of hotels is: on three star - 8 years; On five-star - no less than 13-15 years old.
These and other well-known, successfully located hotels have cafes, restaurants and bars, equipped places for recreation, casino, etc. Less popular hotels of smaller sizes, located not in such prestigious areas, usually assume housing and maintenance of higher quality and have their own customers.
3. Garages - Parking (auto parking) As commercial real estate in the country is practically not evolving, although the prospects are available. After all, for each thousand inhabitants, about 150 parks are required in accordance with the norms.
Currently, for example, in St. Petersburg, less than 60 / per park of passenger cars have places of constant storage, of which only 2% are located in underground garagesAlthough the need for them is very high. Due to the high cost of the machine-space (4-6 thousand dollars, and in the city center, prices reach 10 - 12 thousand US dollars) of the mass construction of autoparkings are not observed. Calculated on the mass client, the value of one machine-place should be within 2 - 3 thousand dollars, i.e. make up about 30% of the cost of the car. Note that re-informing the single garage box is currently extremely difficult, because GU "City Bureau of Registration of Real Estate Rights" (GGB) registration of garages is not engaged. To solve this problem, you need to create unified system Registration of property rights to garages of various types.
4. Shops and shopping complexes. As the experience of major cities in Europe showed, good conditions for the location of multifunctional shopping centers (MTC) are: intersection of large motor vehicles, the immediate proximity of metro stations and stops terrestrial transport. Most often, such centers are located in the "bedroom" areas, or outside the city, in fact on the wasteland, near a large highway. In the US, MTC ("Mall") are usually located beyond the city, which can be explained by a certain number of vehicles on soul of the population, population population and other factors. These differences, respectively, affect the requirements for the formation of a common ITC strategy during business planning, design and promotion, and during the construction and operation of the shopping center. For example, the number of parking spaces will be different, the presence and parameters of recreation areas and entertainment, related domestic services, etc.
To the factors that determine success can be attributed:
- Properly selected location;
- drawing up a functional solution and accumulation - the needs of potential visitors;
- a properly compiled forecast for the development of the territory adjacent to the construction site (for 5-10 years);
- the total atmosphere of MTC, which is achieved in the design and design development process;
- clearly worked out of tenants;
- The correctly chosen management company.
For shopping complexes, it is especially necessary, other than those listed factors, also providing service services to their tenants (for example, permanent cleaning of the territory, repair service, 24-hour security, Cardboard pressing, etc.). In the St. Petersburg market, the largest trading complexes providing the above services are "Balkan" and "Ladoga". Thus, trading complexes can be both trade and market and trade and entertainment.
It should not be considered that the development of multifunctional shopping centers is the invention of the West. It is well known that the tradition of the development of large retail premises, passages, courtyards, where "any kind" visitor could acquire everything that his soul, in accordance with the needs and income, where it would be possible to show "on others to see and show themselves roots in the past.
Regions of the country are in different economic conditions and are developing in their difficult laws, therefore, in modern Russia, the process of the emergence of new or modernization of old shopping centers is non-uniforms. Moscow is leading in this process as a global megalopolis that exists compared to other cities of Russia in the highest investment favored.
Trade, as the scope of economic life, is least susceptible to the influence of negative economic and political changes and quickly recovers from the crisis and depression, and the main indicator of the development of the trade sector can be considered a growing demand for functional, safe trading areas.
Currently, in the total volume of non-residential Fund of St. Petersburg, sales of commercial purposes takes only 7.2% (see Fig. 1.2). As a result, the provision of residents of the city by trading areas is 0.68 square meters. m per person. For comparison: in Helsinki per person accounts for 3.5 square meters. M - five times more than in St. Petersburg.

Fig. 1.2. The share of trading areas in the overall structure of non-residential fund (according to GUION and IIC "Real Estate Petersburg")
Problems that cause deficit of liquid and promising to invest in trade real estate in most cities of Russia are similar and are associated primarily with the structure of the non-residential foundation in the pre-reforming period:
Under profitable entrepreneurship, a small share of non-residential premises is given, a large part of which is occupied by various organizations;
Unsatisfactory location of many objects that are functionally suitable for commercial use, does not allow them to develop;
In large industrial cities in the structure of non-residential foundation, the proportion of industrial real estate, the republic of which requires significant investments and is often difficult due to an unclear legal status;
Most of the non-residential foundation is in unsatisfactory technical condition;
In most cities, investment activity is focused mainly in the city center.
For example, in four central regions of St. Petersburg there are about 40% of trade enterprises (Fig. 1.3). At the same time, their share accounts for only 25 / on urban retail space, although it is in the center that three most extensive department store are located - "Living Dvor", "Passage" and DLT. In the historical part of St. Petersburg there is not a single modern shopping center that meets Western requirements.

Fig. 1.3 Share of the Center in the structure of trading enterprises according to the Committee on the Consumer Market on 01.01.99
Today, stores with an area of \u200b\u200b100-200 square meters are in the greatest demand. m., further, descending - less than 100 square meters. m. And in the range of 200 - 400 square meters. m. area of \u200b\u200bmore than 500 square meters. m less in demand. Among the main requirements of tenants are display windows and parking.
If you proceed from the optimal area of \u200b\u200ba store of 400 square meters. m, then about 300 square meters. M should have to accommodate 100 square meters. M - on utility rooms, 70 square meters. M - on warehouses and 30 square meters. M - on cabinets.
An adjacent infrastructure affects the choice of place to rent a shop. For example, located in the very center of the city on the "deadlock" streets or in alleys, objects remain out of sight of interested tenants.
5. Industrial (industrial) real estate in Russia is in the initial stage of development, Although recently, by the bulk of privatization objects, the owner is determined. Before entering into a deal, it is necessary to carry out a comprehensive analysis of the right-point documents to make sure that the seller's rights are incidentality to the proposed object, the possibility of its legitimate alienation and the rights of the new owner to use this object on the intended intended purpose. As the process of forming a real owner develops, the volume of transactions in this area will increase. But this is one side of the question. On the other hand, almost every city can observe empty buildings of factories and factories in 5 - 8 floors with dilapidated and (or) engineering networks and knocked out windows of windows. They stand and do not find an effective owner. Why? There are several reasons:
1. Industrial building 60 - 80 GG. Does not meet the requirements modern technologies, and reconstruction requires large capital investments.
2. Currently, the main consumer of industrial real estate is small enterprises that require real estate objects of certain specifics for their development: high capacity, presence of railway driveways, single-storey and preferably worthy buildings with autonomous communications.
3. As a rule, the requirements of potential tenants are overestimated and does not correspond to the proposed industrial facilities.
4. Industrial real estate owners offer objects in a deplorable state, and at the same time establish overestimated prices.
5. More or less complete and accurate information on industrial real estate, its legal status, sizes, condition, etc. absent.
All this gives the natural real estate market is a natural and unpredictable nature.
On the formed Western market, another, differing from the above classification of real estate objects by categories A, B and C.
Real estate facilities used to maintain a specific business. Usually sold together with business (specialized real estate);
Non-specialized real estate - ordinary buildings - Magazines, offices, factories, warehouses that are usually sold or rent.
Public buildings and structures of various types and species have more than 3000.
Order of the Kuga St. Petersburg dated August 24, 1998 No. 1289-R "On the procedure for issuing a passport of an object of unfinished construction".
Order of the mayor - Chairman of the Government of St. Petersburg from 19.10.94 No. 1043-R "On the procedure for the implementation of the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of July 22, 1994 No. 1535 in terms of the sale and rental of land plots."
Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of 11.05.95 No. 478 "On measures to ensure guaranteed admission to federal budget Income from privatization "significantly reduced the regulatory price of land at the sale of land located under privatized enterprises.
In accordance with the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of July 22, 1994 No. 1535.
The classification of real estate objects on various features (criteria) contributes to a more successful study of objects. For these purposes, you can apply different principles of classification depending on their origin and destination. The classification of real estate objects is carried out on four main features:
Origin;
Appointment;
Scale;
Readiness to use.
By origin, distinguishes:
- natural (natural) objects - Plot, forest and perennial plantings, separate water bodies and plots of subsoil. These real estate objects are also called "real estate by nature";
- Artificial objects (buildings):
but) residential Properties - A low-storey house (up to three floors), a multi-storey house (from 4 to 9 floors), a house of high floors (from 10 to 20 floors), a high-altitude house (over 20 floors). The object of residential real estate can also be a condominium, section (entrance), floor in the stairwell, apartment, room, country house;
b) commercial real estate - offices, restaurants, shops, hotels, garages for rent, warehouses, buildings and structures, enterprises as a property complex;
in) public (special) buildings and structures:
- medical and wellness (hospitals, clinics, nursing homes and houses of a child, sanatoriums, sports complexes, etc.);
Educational and educational (kindergartens and nursery, schools, schools, technical schools, institutes, houses of children's creativity, etc.);
Cultural and educational (museums, exhibition complexes, parks of culture and recreation, houses of culture and theaters, circus, planetarium, zoos, botanical gardens, etc.);
Special buildings and structures - administrative (militia, court, prosecutor's office, authorities), monuments, memorial structures, train stations, ports, etc.;
d) engineering facilities - Meliorative structures and drainage, integrated engineering preparation of the land plot for development, etc.
Each of these groups can be subjected to further division based on various typological criteria.
Artificial facilities were called - "Real Estate by Law", but this real estate category relies on "real estate by nature".
Artificial objects can be fully built and ready to operate, may require reconstruction or overhaul, and also relates to unfinished construction facilities (incomplete). To "incomplete" refer objects for which in the prescribed manner are not issued by the acceptance of an object of operation.Objects of unfinished construction can be divided into two groups:
- objects on which work are underway, and objects for one or another reasons are discontinued. In accordance with the current procedure, there are two types of termination of work at the facility: preservation and complete cessation of construction. Decision on termination of construction takes an developer. The solution should indicate the reasons for conservation or complete cessation of construction, as well as:
In conservation - the term for which is preserved (temporarily stopped) construction, conservation conditions, the name of the organization on which the construction preparation is assigned to the conservation, the safety of constructed objects and work performed;
With full termination of construction - the procedure for the elimination and use of already constructed objects or their parts, mounted structures and equipment, implementing material values \u200b\u200bdelivered to the construction site.
Land plots can be divisible and indivisible. The plot is called divisible when it can be divided into parts and to form independent land plots with the permission of targeted use. In accordance with the legislation, the section of urban lands, land farms, etc.
The land fund in the Russian Federation for economic purpose is divided into seven categories of land:
1. Agricultural land Have a special legal status in the real estate market and are used:
For agricultural production (pashnya, hayflowers, pastures, deposits, perennial plantings, virgin and other land);
For personal subsidiary economy;
For collective gardening and gardening;
For utility agricultural production;
For experienced and scientific stations.
Land translation from this category to another is carried out only by the decision of the subject of the Federation. Particularly valuable lands are not subject to privatization.
2. Lands of cities and settlements occupy 4% of the country's territory. These lands are located residential buildings and socio-cultural institutions, as well as streets, parks, squares, environmental structures; Industrial, transport, energy, defense facilities and agricultural production can be placed. This land category provides 86% of income into the consolidated budget from all payments for land use and can only be used in accordance with the general planners and projects.
3. Industry, transport, communications, television, computer science and space support, energy, defense and other purposes. Have a special use mode.
4. Lands of specially protected territories include reserves; Green cities, rest houses, turbases; Monuments of nature, history and culture; Mineral waters and medicinal dirt, botanical gardens, etc. This category of land is intended for the improvement of people, mass recreation and tourism, as well as for historical and cultural education and aesthetic pleasure. Such lands are protected by special legislation, and lead economic activities They are prohibited.
5. Lands of the Forest Foundation are fully determined by the legal regime of forests growing on them. This category of land includes land covered with forests and provided for the needs of forestry and local industry.
6. Lands of the Water Fund. These are lands engaged in reservoirs, glaciers, swamps (except tundra and timber tundra), hydraulic structures and rope strips with them.
7. Earth stock serve as a reserve and stand out for various purposes.
The sale of land, as well as the allocation of them for entrepreneurship and transfer from one category to another, is carried out in accordance with the laws of the Russian Federation and the subjects of the Federation.
The plot in the turn is used to obtain income, including by transferring to rent, introduction to share capital, to ensure pledge, etc.
In each municipal association, the territory is divided into zones depending on its value. For each zone, its tax rate is installed.
In the course of operation, the land plot may bring income, called land rent. Under it it is understood as the internal indicator of the efficiency of the use of the land plot as, an asset of an enterprise, which is calculated as private from the division of the calculated value of the value for the period of capitalization.
With regard to residential real estate objects, several typological constructions are possible. For example, depending on the duration and nature of the use of housing:
Primary housing - a place of permanent residence;
Secondary housing - Country housing used for a limited period of time;
Tertiary housing is intended for short-term accommodation (hotels, motels, etc.).
In relation to the conditions of large cities, it is customary to allocate the following typological characteristics:
1. Luxury housing.
The following basic requirements are presented to it:
Accommodation in the most prestigious areas of the city;
Belonging to the "old" foundation (in the presence of a capital repairs and reconstruction) or to the "Stalinist" fund;
Brick walls;
The total area of \u200b\u200bapartments is at least 70 square meters. m.;
The presence of isolated configuration rooms approximate to the square, and a large kitchen (at least 15 sq.m.);
The presence of a protected entrance, an underground or nearly located garage, etc.
For low-rise cottage-type houses that are part of elite, such consumer requirements are characteristic as:
Accommodation at such a distance to the city when the trip takes no more than 1 h;
Brick walls;
Development in two or more levels;
The presence of household and engineering facilities.
2. Housing of high comfort.Consumer demand for housing this type involves the presence of the following basic characteristics:
The possibility of accommodating in various (not only the most prestigious) areas of the city;
Some reducing requirements for rooms and kitchens up to 12 and 8 square meters. m (respectively);
The presence of a living room with an area of \u200b\u200bat least 17 square meters. m.;
Large variety of structurally technological parameters.
In relation to low-rise buildings, located in the suburban zone, the main characteristics is high strength, durability and low thermal conductivity of walls, as well as engineering networks.
Typical housing.It is characteristic of:Accommodation in any area of \u200b\u200bthe city;
Compliance of architectural and planning parameters with modern building standards and rules;
According to constructive technological parameters, belonging to the houses of the second generation of industrial house-building and modern.
For low-rise suburban construction, not only technical characteristics, but also the security of the main objects of socio-domestic destination are the most significant.
4. Housing of low consumer qualities
Based on the conditions of consumer demand formed under the influence of the solvency factor, the requirements for this type of housing are very small:
Accommodation in non-varying areas;
Distance from major transport communications;
Belonging to such constructive technological types as the buildings of the "old" fund, not subjected to capital and repair and construction work, and the house of the first generation of industrial home-building;
Accommodation in the first floors of other types of houses;
Understated architectural and planning characteristics, etc.
The considered classification takes into account the preferences of the target groups of housing consumers and the level of their solvency (marketing approach). However, residential real estate can be distributed on the basis of urban benchmarks.
So, when making economic decisions in the residential real estate market, typology is used, including:
Houses "Old" Foundation, built in the pre-revolutionary period;
Houses built for the period from 1917 to the late 30s, distinguished by laconicism of architectural and planning solutions located in close proximity to the place of application of labor (of the period), little more prestigious, but possessing high constructive and technological characteristics ;
- "Stalinist" houses, the term of the construction of which came for the period from the late 30s to the end of the 50s., Concerning the revival of classical architectural and urban positions and located mainly in prestigious, distant areas from industrial areas;
Houses of the first generation of industrial home-building (60s) (Khrushchev), characterized by understated architectural and technological parameters;
Houses of the second generation of industrial house-building, built in the 70-80s, when higher norms and standards were used in urban planning;
Modern residential buildings, distinguished by a large variety of characteristics.
There is I. classification of residential real estate objects depending on the material of the exterior walls of the building:
Houses with brick walls;
- panel houses;
Monolithic houses;
Wooden houses;
Mixed type houses.
Separate niche occupy objects of suburban real estate due to a minor transaction volume and their specificity. Basically, secondary housing is presented here.
Many factors affect demand and supply in this market sector. In addition to ordinary priorities when buying residential real estate, personal interests are of great importance to location, the time of year, the social homogeneity of the neighbors. Buyers pay great attention to the presence of a complete range of communications (autonomous systems of heat and water supply). Preference is given to objects of brick or wood. As a mandatory attribute, a minimum of 10 acres is considered as a mandatory attribute to the suburban real estate.
Signs of the classification of residential real estate that served as the basis for grouping is different, as well as their motivation, preferences and solvency conditions. Use a single typological criterion that integrates the influence of all factors is not possible. Therefore, in practice there are several criteria that give a reasonable idea of \u200b\u200breal estate.
Commercial real estatein Russia, it became formed only with the beginning of the privatization of enterprises. The commercial real estate sector is much smaller than residential, therefore transactions, respectively, although worldwide commercial real estate is the most attractive. It should be noted that in this sector the prevailing form of transactions is rental.
Commercial real estate can be divided into revenue - actually commercial real estate and creating conditions for its extraction - industrial (industrial) real estate.
Real estate that makes income can be attributed:
1. Office space. When classifying office premises in each region, the municipality is accepted by various factors for which the room refers to a particular class. It may be location, quality of the building (finishing level, facade, central entrance, availability of elevators), management quality (management company, the availability of additional services for tenants) and others. Among the factors that affect the attractiveness of office space, allocate a number of positive and Negative sides, which are presented in Table 10.
Table 10 - Positive and negative sides Office accommodations affecting the cost of renting or selling
2. Hotels. Hotel projects today in the Russian Federation are the most complex types of investment in rectic real estate. Construction of new or reconstruction of old hotels in the highest class, their equipment and operating costs are considered a fairly risky investment, because The costs of such projects are several times higher than the cost of building trendy shopping complexes or office centers. In addition, five-star hotels have a very long payback period, so the Russian revenue real estate market is a low tariff hotel and lower capital investments.
To date, the hotel complex of large cities is very divergent and includes objects of various categories. Most of these hotels are small. Many hotels have cafes, restaurants and bars, equipped seats, casino, etc. Less popular smaller hotels are located, as a rule, are not very prestigious areas and provide accommodation and maintenance of higher quality and have their customers.
3. Garages - Parking (auto parking) As commercial real estate in the country is practically not evolving, although the prospects are available. After all, for each thousand inhabitants, about 150 parks are required in accordance with the norms.
Common for all major cities is the growth of the fleet of cars owned by the population. Many families have two - three cars. However, there are not enough places for parking. This is connected with the features of the construction, and with the peculiarities of the presence of free land in the city feature.
4. Shops and shopping complexes. As the experience of major cities in Europe showed, good conditions for the location of multifunctional shopping centers (MTC) are: intersection of large motor vehicles, the immediate proximity of metro stations and land transport stops. Most often, such centers are located in the "bedroom" areas, or outside the city, in fact on the wasteland, near a large highway. The factors that determine the success of the placement of MTC can be attributed:
Properly selected location;
Drawing up a functional solution and accumulation - the needs of potential visitors;
Corrected forecast for the development of the territory adjacent to the construction site (for 5-10 years);
The total atmosphere of MTC, which is achieved in the process of designing and design development;
Clearly worked out the selection of tenants;
The correctly selected management company.
For shopping complexes, it is especially necessary, other than those listed factors, also providing service services to their tenants (for example, permanent cleaning of the territory, repair service, 24-hour security, Cardboard pressing, etc.). Trading complexes can be both trade and market and commercial and entertainment.
Trade, as the scope of economic life, is least susceptible to the influence of negative economic and political changes and quickly recovers from the crisis and depression, and the main indicator of the development of the trade sector can be considered a growing demand for functional, safe trading areas.
Today, there are 100-200 sq. m. And in the range of 200 - 400 square meters. m. area of \u200b\u200bmore than 500 square meters. m less in demand. Among the main requirements of tenants are display windows and parking.
If you proceed from the optimal area of \u200b\u200ba store of 400 square meters. m, then about 300 square meters. M should have to accommodate 100 square meters. M - on utility rooms, 70 square meters. M - on warehouses and 30 square meters. M - on cabinets.
An adjacent infrastructure affects the choice of place to rent a shop. For example, located in the very center of the city on the "deadlock" streets or in alleys, objects remain out of sight of interested tenants.
5. Industrial (industrial) real estate in Russia is under development, Although recently, by the bulk of privatization objects, the owner is determined. Before entering into a deal, it is necessary to carry out a comprehensive analysis of the right-point documents to make sure that the seller's rights are incidentality to the proposed object, the possibility of its legitimate alienation and the rights of the new owner to use this object on the intended intended purpose. As the process of forming a real owner develops, the volume of transactions in this area will increase. But this is one side of the question. On the other hand, almost every city of the country can observe empty buildings of factories and factories in 5 - 8 floors with dilapidatives and / or unfastened engineering networks and stamped windows of windows. They stand and do not find an effective owner. Why? There are several reasons:
1. Industrial building 60 - 80s. Does not meet the requirements of modern technologies, and reconstruction requires large capital investments.
2. Currently, the main consumer of industrial real estate is small enterprises that require real estate objects of certain specifics for their development: high capacity, presence of railway driveways, single-storey and preferably worthy buildings with autonomous communications.
3. As a rule, the requirements of potential tenants are overestimated and does not correspond to the proposed industrial facilities.
4. Industrial real estate owners offer objects in a deplorable state, and at the same time establish overestimated prices.
5. More or less complete and accurate information on industrial real estate, its legal status, sizes, condition, etc. absent.
All this gives the natural real estate market is a natural and unpredictable nature.
On the formed Western market, another, differing from the above classification of real estate objects by categories A, B and C.
Real estate facilities used to maintain a specific business. Usually sold together with business (specialized real estate);
Non-specialized real estate - ordinary buildings - shops, offices, factories, warehouses that are usually sold or rent.
Ethnology
"Land marks" and "Road Tags": ground natural and artificial objects in a spatial orientation system
Tundra Nenets1
V.N. Adaev
The set of ground natural and artificial landmarks used by nonsense, as well as their memorization and use practices. Considered by K. V. Istomine and M.J. Twileer two-level knowledge of the terrain of the tundra nonsense, where the upper level allows you to move around the territory without difficulties, and the bottom contains detailed knowledge of the landscape necessary for reindeer herding. It is concluded that the universal and priority natural benchmarks for the tundrants are rivers and hills.
Spatial orientation, tundra nonsense, northern landscapes, conditional signs, roads.
Nenets, like some other indigenous peoples of the world, earned the fame of masterly oriented people, whose talent is not to be knocked out from the right direction in the absence of visible landmarks (in the conditions of the polar night, in Purga and Fog) became legendary, and for him see each other not superflueline . The Nenets deep knowledge of northern land and the experience of orientation in space from the very beginning were in demand by Russian immigrants to Siberia. The very development of the Yamal North could not take place without a mandatory person from the number of indigenous inhabitants - "Tolmach and the conductor", which accompanied the expedition, starting from the early period and up to the first decades of the twentieth century.
Meanwhile, the orientation system of the Nenets population is still remaining the topic that has not studied specifically. In this work, first of all, on the basis of the field materials of 2014, collected in Nadym, Tazovsky and Yamal regions of the YanaO2, a set of terrestrial natural and artificial and artificial landmarks used, as well as their memorization and use practices, are considered. The methodological basis of the study is similar work on the ethnographics of other peoples as our country [Kulezin, 1998, 2000; Lavrille, 2010; Istomin, Dwyer, 2009] and abroad [Lebedev, 2008; Allen, 2000; Aporta, 2003, 2009; Leroi-Gourhan, 1993; and etc.].
Basic terminology
As the closest equivalents, the concepts "to navigate" participants were recorded by the participants of field research. For the term "landmark" there are two main versions: I "faderbava (" lands label "), in a simpler version - inadvertently", faders "Ma (" Tag "); SEHERS TYA" UY ("Road signpost"). Nuances The differences in the terminology will be covered below. In the NM. Tereshchenko is represented by another synonym for the same concept - PUN ("Landmark", "sign"), derived from which the verb, Punoo, means "use anything as a guideline."
The work was performed with the support of state contract No. 24K-2905/2014 dated July 3, 2014. "Archival and field research of the orientation system in the space of the autonomous districts" and Grant RNF No. 14-18-01882 "Mobility in the Arctic: Ethnic Traditions and Technological Innovations "(Hand. ChL-Cor. Ran A.V. Khovnev).
Field fees were carried out by E.A. Volzhanino (Yamalsky district), R.Kh. Rakhimov and author of this article (Nadym and Tazovsky district). I am grateful to teachers of the Nenets language of the Tazovskaya boarding school M.Kh. Salinder, etc. Zherrydarova, an employee of the Scientific Center for the study of the Arctic S.E. Sirpivo and philologist N.I. Vella for help in the editorial office of nonsense words and expressions.
Natural landmarks
The longer the Nenets live in one area, the more detailed knowledge of the terrain, its landmarks, the landscape outlines he has. The thorough knowledge of its land is reinforced by a very fractional toponymic baggage. Moreover, these names often indicate the specifics of the geographical object, its distinctive features and qualities, for example: Nuna-Yah - a calm river, a whale-sled - burned housing, Hasreo - a wetlasting lake, etc. In some cases, as indicated by G.P. Harechi, Toponym carries an important warning for a person: Ilena I ("Living Earth", i.e. Bogox); Labatsgans need (slamming mountain); You need Handanda (wolf's hill or "Sotka, where many wolves").
From the statements of the Nenets: "Each lake, every river, every river, every holmik - have its own name. And every holmik, every river - they differ from each other "[PM Adareva, Tazovsky district]. When communicating with one of the reindeer breeders, which was forced to learn the landscapes for themselves to develop new landscapes for himself, we asked him to bring the specific distinctive features of the surrounding rivers. The following answer sounded: "The riches are the same no, they are all different. Here is this river, where we are now standing, it is narrow, and the previous one was wider. If you get to the river, it is not everywhere you can find a ferrod, there it is impossible to find in winter. And here the other side is visible. Even if the rivers are about the same size, then they are all different. Suppose that this river and that, they are a bit identical, but there is still something different: soil, trees there ... In one place there may be high, in another lower, or in one place there may be a yagelnik, and In another moss [PM Adares, Tazovsky district].
Accordingly, in detailed knowledge of the terrain, the person can easily, at a smaller number of visible objects, determine their location in conditions of limited visibility (night, blizzard, fog, etc.).
In the overall massif of the landscape, there are always the most outstanding points that allocate this area from the surrounding, facilitate her memorization. Often, as such, the highest objects visible at a large distance are hills (seds, sitting), hills or ridges (Xa): "For example, hills. The hills are different - low, high. There are big hits. Kilometers for 10-15 can be seen. In the kilometers of three will be so visible - just look to be visible. Such sopes are seds. All - Seda. They have their own names. You can say SI "Yves Seda - seven fellows such nearby. Or Yakhasha" - these are twins. They all have names, so they focus. In some places within a radius of 10 km in one place, and in others there is no "[PM Rakhimova, Tazovsky district].
With a high focus of sobes in one place on the fore. Their certain notable qualities are already published: absolutely naked, with a tree on top, double, etc. Sometimes stocks may have even more outstanding features: "Sideyahs have two sacred holy sings. They are growing. One step is visible constantly, and the other is only in the evening. It is directly noticeable as it appears "[PM Adares, Tazovsky district]. The relevance of the tundra hills as a landmark is confirmed by the phrase, which is present as an example of the use of the word Hoi ("Hill") in the NM Dictionary. Tereshchenko: Hoim "Puno" Padm "(" I used a hill as a guideline ").
In the southwestern part of YanaA, a great high-altitude reference point are the protrusions of the Ural Mountains (Raverka PE), which are visible in clear weather for many tens of kilometers. For example, for nonsense Bidarats, the tundra is so well distinguishable from a long distance the object is the Mount Baydarat-Saurea, located in the upper reaches. Baydarat. For the characteristic profile, the Nenets sometimes call it in Russian "Triangle". In the book V.P. Evladva shows a story about the long journey of the Nenets boat hunters. When, after the storms, the Nenets managed to finally go to the shore, before them the unfamiliar area appeared and they were able to determine their location only thanks to the knowledge of the Mountains of the Urals: "The tea began to heal. Suddenly - on five deers of Nart. We see - Zyryanin with a boy. In self-named, does not say, he also does not know how, and we do not know. He only replied that the Holy Stone Minisa is nearby. Fog scattered. The minis is seen. Under the Urals got! " [Evbabi, 1992, p. 42]. On the large space of the Peninsula of Yamal a good visual guideline is the Ridge Yamal-Hoi - extension from the north to the south hill on the watershed between Kars and Ob Water Systems. Similar far benchmark (chain of hills on the horizon) used, apparently, Nenets conductors A. Shrenka in Arkhangelsk
tundra: "An open view here has no boundaries, like on the surface of the sea, and finds an obstacle only in the blue-eyed fog, where the barely worrying line disappearing in a pale sky, there and Syam denotes the top of the hills and serves Samoly the faithful compass on this TundRec ocean "[Schrenk, 1855, p. 253].
We also note that all the above-mentioned hills are used by the Nenets and for the survey. Since they are best visible on the distant distance, a coherent system of the mutual position of elevates is formed in the memory of the Nenets, with the knowledge of the relative height of objects, the maximum distance on which those are visible, the singularities of the outline from different directions, etc. It is not by chance for their standings, reindeer herders prefer to occupy dominant heights with a good overview.
Extremely much attention in the orientation of the Nenets pay rivers. It is the rivers that are the starting guideline from which the study of an unfamiliar area begins: "In a new place first remember the river. When you go in an unfamiliar place, you turn around the river, you already see what is where is the shores that are rippled, overgrown, sandy. In the other side, in the south of Taimyr, there are banks - ruling, there is a rocky land already begins "[PM Adares, Tazovsky district].
It is important to note that the tundroviks at the memorization are concentrated primarily on the structural system of the river basin, the general direction of the flow of its watercourses relative to the parties to the light. The specific drawing of the river bed is seen, as a rule, very schematically. In particular, this approach is typical for reindeer herders, but, oddly enough, it is found to a significant extent in nonsense fishermen. When those at our request were painted the system of the dummy and islands of the low-level r. The pelvis, according to which they are constantly moving, the outlines of the Earth and the bends are also schematically shown in many respects, without attention to the details. At the same time, on the spot, the same fishermen are well oriented in a complex duct system, they know all dangerous places.
The question is, of course, requires a more detailed analysis, but at this level of familiarization with him a significant difference is noticeable in the principle of memorizing river systems and the level of detailing these knowledge between the nonsense and representatives of the typical Taiga peoples of Siberia (Khantami, Mansi, Evenks, etc.). The observation of one of the researchers ethnography Evenkov A. Lavrille: "Wanting to help them (Eventers. - V. A.) to navigate, I, in accordance with the system of orientation of my own culture, pointed it to the four sides of the world and the highest points , But they answered me: "We are not interested in neither the starting points nor the mountains, we are interested in rivers!" In addition, I noticed that they, despite belonging to a particular generation, very quickly found large and small rivers on the map, which were interested in the stream configuration (allocated by me. - V.) ... I noticed that adults and children, men and women often repeatedly repeated as a table of multiplication, the connection of rivers and rivers covering the space, much superior to the territory that they were in their nomadic life. " This kind of information can be easily found in other ethnographic work on taiga peoples (see, for example: [Kulezin, 1998, 2000]).
For comparison: None of the surveyed tundroviks expressed confidence that he could identify any river on the map from the surroundings known to him only on the total figure of the flow. In order to start working with a topographic map, reindeer herds, as a rule, it was necessary to see where the nearby large river and some second landmark on it (settlement, inflow, etc.) is located on it. After that, they could already correctly indicate its tributaries and their present location.
There are interesting nuances associated with oriented by rivers. As you know, the course of the river is usually a winding and prevailing direction of the bed can not always be clearly represented by seeing only a small river area. Nevertheless, the occasions are exclusted - rivers with a pronounced direction from the source to the mouth. Such reservoirs become for nonsense not only with good guidelines (as the object standing out from the general environment and as a direction indicator), but also convenient roads In winter, since it can be driving constantly on the line, without the need to depart ashore to cut the big loops. For such rivers, the Nenets marked a special name: "Some rivers, like that in the top I got up - we have such a straight river Hutin, - you can see as well there, far. Other rivers will not see that. And here, the father showed. Here, Hutin means "straight river". And there is another, Haralyang ("winding". - V. A.), infinite
turns there. It is really Haralyang. It is better not to descend even on deer. So, along the river you go. God forbid to go down to her - from there you will not go out, is Natural Haralyang "[PM Rakhimova, Tazovsky district]. In general, in the territories of "naked" tundra for inexperienced, few familiar with the terrain of people exactly the rivers became the main roads.
"Format" of information about the watercourse stored in the memory of the tundra nonsense, and how this information is used by them can be illustrated by the next statement of one reindeer breeder: "At the river, you still need to know how to know how many of them! Without this you will disappear. I'm when I'm going in the dark, I think: yeah, the first remained, the second I should pass the third, and the fourth I have a chum on a fork where she went with a big river. And exactly I get "[PM Adares, Tazovsky district]. It is significant that the expression "count the rivers" was used by almost all the tundrants in their stories about how they are oriented in a complex network of small rivers.
The author shares the opinion of Ethnographers K.V. Istomy and M.J. Twisters, which, analyzing the materials on the ethnography of the Nenets of the Tazovsky district, suggested that it was the rivers that make up the main axis of the mental card of nonsense reindeer herders. And in this mental map of the Nenets, the researchers allocated two hierarchical levels: 1) the upper submitted by a hydraulic system, where objects and territories are linked to adjacent watercourses; 2) Nizhny, which presents a detailed map of any territory limited by several neighboring hydraulic systems. The reindeallers themselves also felt this two-level knowledge of the terrain, where the upper level ("knowledge of rivers") is publicly available and allows you to move throughout the territory, and the lower level ("knowledge of the earth") contains detailed knowledge of the landscape, only owning which you can deal with either a tundra area of \u200b\u200breindeer herding. Similar information was obtained during our field research.
A good landmark for the Nenets can serve as lakes. This is especially true of territories where they are focused in large quantities. About the specifics of memorizing a place in one of the similar ranges (southern Taimyr) told Taza Nenets: "When you fly on a helicopter - there are generally a lot of lakes there. Like this water, it is all solid everywhere. The lakes are also unequal: separate stretching a few kilometers, on the other there is the island there - with the edge, the island is there, even two islands happens. And then you go, remember that if the river drove, then there should be a lake "[PM Adares, Tazovsky district].
Lakes remain landmarks and in winter. Considering their strong notice of snow, smoothing the outlines of the relief, limited visibility under the conditions of the polar night, sometimes it is possible to determine their location with the help of these objects it is difficult and experienced tundra. Sometimes, to clarify the reindeer herds, they resort to the old tried method: to try the snow with the back side of Korea, on which a metal tip in the form of a spear with a stupid edge will be put on the tradition. Similarly, they determine their location in the river lip.
There are some other distinct landscape benchmarks that are successfully used by the Nenets. For example, the last groups of larchs on the border of Ferotandra with Tundra (similar places are well known to the Nenets), multi-kilometer broad stripes of the shrub on the watersheds of the rivers, the line of the coast of the sea or lips. We give one of the removal of tundroviks as an example: "Here, near the righteous river, we have a strip of Aalchovenik - 10-15 width kilometers. It seems to be separated: naked tundra begins to the north, and to the south - Latstone. If you go and saw that Olchovenik went, - this is in the direction of the pelvis already, and then, for Olhovnik, the rivers went to the side of Mesocene. Here you will not make a mistake, in which direction to go. Man, if all his life lived in Tundra, he already knows all these "tracking sites" "[PM Adareva, Tazovsky district]. The shrub is also the main identification sign of the coast while in the snowy water area of \u200b\u200bthe sea or lips. Nenets, unsure in their abilities correctly navigate the ice expanses, if possible, prefer to move within the visibility of the coastal shrub line.
To a certain extent, the Nenets are used as landmarks and ravines. They are most noted on the spaces of open tundra. On this, in particular, paid attention to one of the reindeer herds of Fondra: "I went to my wife, I have it from the find. They already have a naked tundra begins, there are practically no shrub there, so I remembered. The difference is that they need to memorize on the hills, rivers and ravines "[PM Adares, Tazovsky district]. IN
a whole knowledge of ravines is more relevant to build a rational, secure route: "We don't know the places - you can climb into extra ravines."
The usual action for the Nenets is to memorize trees or shrubs of an unusual form (with a stem, "like an eagle nest", with a curved form, etc.) or standing separately from others, since such an original object is also a good rising area: "Suddenly there is a tree There is one thing - the best option. "
Research materials suggest that the universal and priority natural benchmarks for the tundra nonsense are rivers and hills. It is significant that only the rivers (streams) and hills appeared in the area of \u200b\u200bthe terrain, which was done for V.N. Chernetskova Yamal Nenets, when they advised him about the trip at the mouth of the river. Tyutey Yah. It is curious that the hills in this figure were depicted in the profile, thereby showed their recognizable outlines [sources ..., 1987, p. 98].
Returning to the above K.V. Istomine and M.J. Twister of the Nenets system of two-level knowledge of the terrain, it must be said that sometimes the transition from the top level ("knowledge of rivers") to the lower ("knowledge of the earth") of the nonsense on their own, by the method of trial and errors. In cases where a person without help is forced to develop a new territory for grazing deer, he for several years is systematically engaged in its detailed study by selecting optimal routes. In front of the nomad to a new place, the reindeer breeding makes walking out of 10-15 km to evaluate the quality of pastures, determine convenient crossings through rivers and parking lot: "Well, I usually in those places before Cass-hand, first went: You get to the new place, you need to see first. We look, where what kind of river, where it flows, the crossing for deer you look - there should be finely, and so that the shores are not such a shrub. I also put the label there "[PM Adares, Taz-sky rn]. Mentioned at the end of the phrase "Tags" - special landmark signs, a detailed story about which is presented in the next section.
In conclusion of this section, we give another eloquent quotation, demonstrating how the tundroviks operate with their knowledge of landmarks on the way: "Before the departure, the road is still in my head. Sopcons remember rivers. If you are going nearby you don't think, you think in the distance (allocated by me. - V. A.). There should be a hill, or a river, or a vigorous sign. The name of the rivers are all already knowing. Thinking rivers you think. Especially in the dark: "yeah, go to the East River" "[PM Rakhimova, Tazovsky district].
Artificial orientations
This section will feature artificial, including specially made, benchmarks that were established by the Nenets themselves, and those that were constructed by other people (mainly industrial and infrastructure facilities).
Directly with the installation of road marks (lighthouses) in the Nenets language, the verbs of Tyzi are associated - "put milestones" (on the road); Pyat (s) - "place milestones" (stuck in the ground or in the snow bushes or branches on one side of the road to designate the path); Wabta (s) - "plant", "sit down" [Tereshchenko, p. 304, 434, 606]. The traditional conventional signs on the terrain used in the tundra can be divided into two categories: just benchmarks (I "faded -" lands label "or Sheeners faded -" Roads Tag ") and landmarks - direction pointers (SEHERS TYU" UY).
The first category of labels is the most diverse. Tundroviks can stick into the snow into the snow in the snow, the branches are not growing down the branches, "), to establish the deer horn, a stick, to connect several branches in the form of" Xuchika ". In some cases, to increase visibility to tags, bright tissue or other material are tied.
These signs are installed mainly: on congresses from the main road; crossroads; the border of the forest or shrub, noting the beginning of the drove track; the place of the future parking, at the beginning of narrow ducts, which is a yield from a large water object; Sometimes - on the road itself, if there is a danger that it will be strongly interlaced; On places of river crossing. Some Nenets clarified that the labels are mainly for the orientation at night. In general, in a good familiar area, especially where there is a good overview and / or a large number of natural landmarks, the installation of man-made lighthouses is usually quite limited and applies only to inform the people going on after the direction of their movement or the core place. Nenets put in such a label in such conditions so as not to get lost
in general opinion, either completely inexperienced, or those who are not able to navigate from birth - Yohobort. From the story of a young girl who traveled to relatives in Lesothyndra: "I have been told:" Why do you need tags? Setkaya, what? "" [PM Rakhimova, Tazovsky district]. Many of the residents of Lesotandra claimed that they were not needed in their places, the manual guidelines are not needed at all: "We didn't put the labels along the way - there are no roads" [PM Adarev, Tazovsky district].
Nevertheless, nonsense in unusual landscapes are more likely to turn to man-made roads. Thus, on the obsened territory, tundroviks sometimes apply scubries on the trunks of trees or laid on the moss branches. One of the elderly reindeer herders told him how his youth, along with other young women, sent to work at the Northern Tundra's northern regions: "In the Antipoyutin Tundra, when they arrived, put marks on the whole road. We were young, we went, traded the Olchovenik and delivered fishermen on the brigades. Every 50 meters, the stumps were put in order to be seen from one other. "[PM Adares, Tazovsky district]. The above example is most likely not to be attributed to the traditional version of the landmarks, as the use of the Russian word informator in the title of the process: Tamka Whobampava ("Stick").
A special system of road landmarks having the same function has developed in forest nonsense. We briefly bring it here only to compare with the tundra. As Forest Nenets said, all of their similar marks perform one function - denote the close presence of the road or its branch. As a road landmarks, they are used by a special way of the peaks of trees (some, nekkal), laid on the trees of Moss (Imp Na-Vako, "Mokhovaya Head") and conventional trees on the trunks (schapma). Somehow is a label when the tree leaves only the "cap" at the top, all the lower branches are cut. Another version of this label is called Nekkal - in the middle of the crown of the tree, the branches are riveted on both sides, so in the end the silhouette remains in the form of the eight: "Neckle makes a big pine on the road. When 40 ° Claus, the choree slightly burned - they will fly away, small. While you drive, you hit, goes from behind - on the other hand, it will hit, the third knocked - everything, the hat appeared small "[PM Adaeva, Nadym district]. Mokhovaya labels are the most short-lived, especially if they are simply laid in the fork of branches or hanged on the bitch. There is a more long-term option when a small tree is engraved and the moss is clamped into the hemp crack.
The second category, indicators, as clear from the title, carries more additional information about the direction in which you need to move. The three such versions of the road tag were recorded: installed sloping sticks, stuck the head of the head, planted on the fox of the skull. All this may be named after Nenets Shere "Yi (" Road Pointer ").
In the first case, the pointer serves as a set of sticks installed in a special order on the spot, where the Chum (sides, "Chumovish" standing) or on the turn from the main road. Most often it is three or five pegs from several tens of centimeters to a half-meter height, stuck in an increase in one line and tilted in the other way, where people left: "The man scales in the tundra: one stick is small at an angle, the second pinchers and the third still do not - Indicates the direction where man left. You came to the parking lot. Watch: nothing can be seen. Where did the person say? He will put sticks, three vests, and these vests show the way where the road was gone. The lowest - centimeters 20-30 sticks height. And inclined, as if they were so "[PM Adares, Tazovsky district]. The pegs are made of a girlfriend, usually from wood, but there are other options. For example, V.P. Evladov describes chopsticks-pointers from deer horns.
Tags in the form of inclined sticks are mentioned in other well-known sources on the ethnography of nonsense. So, Yu.I. Kushelevsky wrote in the XIX century: "Some Samoyeds leave on chugors (places of parking. - V. A.) a few sticks stuck in the snow tilted to the direction where their new chores should be, and they cut their tamga on these sticks ( Signs), for which they learn, whose Anas (Argish. - V. A.) stood on Chugore. " The given information about personal Tamgh suggests that this method of transmitting information not only had widespread use, but also could be addressed to both a specific person and to uncertain, pretty conditional addressee.
We are similar in fact the pointer is the left head of the head, which, due to its contrasting color, is perfectly visible on the background of snow. The description of this Nenets label is also found in the literature: "Leaving, the shepherd will not forget the most noticeable head of the post
it is so that it will indicate the path of herd. If nearby trees, puts it between the bitch. Strictly adhere to the specified direction - and pic a flock "[Salinder, 1987, p. 40]. A similar function of the pointer on the left side was sometimes performed by a deer skull: "There may be a deer head on a stick to put and turn in the other side where you left. It does not have a special name that she is a label, just a head, and everything "[PM Adareva, Tazovsky district].
According to G.P. Harechi, another conventional sign of the Nenets, who served to attract attention was a piece of matter tied to the choral (Labac). Taza Nenets told about the use of a fire, divorced on an elevation, as a signal for lost people. Nowadays, with the same purpose, a plastic bag tied to a stuck high branch is ignited or attached to the installed six, a light bulb connected to the generator, masses with lanterns, etc.
In addition to special travel marks, there could be some stationary objects associated with the vital activity of the Nenets themselves. The most common of them, roads will be considered separately by virtue of its specificity. The following most important landmarks are sacred sites (Habida I) and Cemeteries (Halmer): "Nenets memorize the terrain on these sacred places, know that there is such something ... then, on burials, in cemeteries. Previously, Nenets were buried, and they are always the road if someone does not know, ask. They: here, the cemetery of such a kind on the road will be, then there is a sacred place (there is a label there - or bones, or something else, larch). And so they found the way, remembered "[PM Adareva, Tazovsky district]. The specifics of the location of the Nenets sacred places - aside from the ones, in itself contributed to the fact that people came down from the way: "Previously, sacred sites aside were from the main roads, such roads, as now, was not. They served as guidelines, they went out when they get lost "[PM Volzhanina, Yamalsky district]. It is important that sacred places and cemeteries are usually located on the hills, many of them remain visible in winter.
Nevertheless, the sacred places, and cemeteries, according to Nenets, pose a threat to a supernatural nature for passing and especially those who stopped next to them. According to this reason, knowledge about the location of nearby sacred places and cemeteries was often used to avoid their close pass during the trip: "You must go to the point, and you should be back the same trail. Not loud, because there are many sacred places. If you turn around, it means that you will have something. Either "Buran" breaks down, or get sick. Therefore, there must be a conductor "[PM Rakhimova, Tazovsky district].
A good reference could be left by the streets in the tundra stocks of firewood, seasonal parking of NART, especially if bright materials were used to cover the cargo in the sleigh. Folded firewood and narts were also usually located on the elevations, because they were not closed for a long time and were visible at a considerable distance.
We are successfully used by nonsense and artificial guidelines set by the received population. The history of the existence of some of them is already very long. In particular, in the book B.M. Zhitkov is mentioned well known to the local Nenets a memorable sign established on the Peninsula Yamal by the participants of the expedition of this year. Malygina 1736-1739: "Samoyeds consider this sign by the business of the" Turman "(Navigar Ivanov) and call him therefore the Yumba Tourman." Modern tundroviks are already faced with a large variety of alien objects, which serve them with reliable landmarks on distant distance: trigopunks (Padladda PAD), drilling rigs, towers cellular communication (especially if there is on top of lighting), large settlements (First of all, the electric light comes from them - Harap [Harichi, 2012, p. 37]), gas torches, pipelines, various other industrial structures, auto and railways, left transport, beams, etc. And local attractions, such as border radar plates in the vicinity of P. Gyda: "We have a" sacred "hill-landmark - these are Army locators Gydan-sky. It appears - everything is going to him and do not get lost never" [PM Rakhimova, Tazovsky district].
Leaving aside the negative impact of the active industrial development on the traditional life and the culture of the Nenets, it should be noted that in such conditions, the locality orientation is greatly simplified: "And the villages are now glowing. Approximately you know where the polarity is, that way you look at the other side - there is Tazovsky and Gazale. If there are a lot of lights, it means there is the road, the track. Only stupid will get lost "[PM Adares, Tazovsky district].
Nenets expensive
The road was always the first landmark and a guide thread, which led in the right direction. In the past, before the start of the industrial development of the North of Western Siberia, there was a saturated network of narted roads - winter (Sheers or Shemers) and Summer (Nappy) in Tundra. Summer due to long-term active use remains well noticeable in the tundra many dozens of years.
In Taza tundra, near the right bank of the lower pelvis, the local attraction was preserved to this day - "Road Wowuli Nenangang" (Wowuli-Naja). The road with a length of about 65 km leads along the coast r. Taz from Oz. Nenaging on the West-North-West to r. Schuye (duct r. Mesiah). On the way, it crosses several large rivers, it comes into an abandoned P. Yaray. When the route coincides with similar old roads, modern reindeer glands use them, as they are laid in the most convenient way, bypassing the crossed landscape, and still remain relatively clean from shrub piglets. It is significant that the long summer roads are all old origin: "There were no wonder even earlier, in those years, when the grandfathers lived - when the forest was taken, the mail, during the years of Soviet power ... And before the Revolution, the Nenets also went far away." [PM Adaeva, Tazovsky district].
Evaluating the high rationalism of the route of old roads, the Nenets emphasize that the people who laid them were distinguished by a special talent: "Some smart man broke through, that's itch that the road passed on the tops of the rivers, where it is straight, where it is better to cut the river" [PM Adaeva, Tazovsky Rn]. By the way, the similar kind of comments on road pioneers are also common among other northern peoples. So, Ethnographer A. Lavrille writes about nomadic events that among them "occasionally there are people with a inventive mind and possessing high status: they know how to open new ways and new territories, having worn by an ax in the forest shorter paths than ordinary nomades. If this way like other nomads, he will soon become a new regular road. "
In the past, Nenets roads could achieve a significant extent. The stories of their grandfathers are preserved in the memory of the reindeer visitors to cities and villages, located in modern Yamalo-Nenets (Obdorsk), Khanty-Mansiysk (Berezov, Surgut), Krasnoyarsk Territory and other regions. According to the reviews of Nenets, at that time (XIX - the beginning of the twentieth century) was not necessary to specially pierce the road to distant places, due to the good sense of the way of communication: "Previously, the father went far. He was not necessary for him to know - there were a lot of people, there were deer around the road. Transport, only deer was winter "[PM Adareva, Tazovsky district]. One of these foaming routes, bonding Ge-Dan with Surgut, described B.N. Towns: "Roads to Surgut are at first along the low-level Poures. To r. Tailova, the influx of Nadym, within the limits of the Samoyed Fundra moving in various ways, followed by one road, as you have to use the existing overwhelms in the forests. This path to which the inhabitants of the cereals of Pura and the pelvis goes, is only a winter road laid predominantly on flames and lakes. In wooded areas, it has the form of narrow pros. "
In the forest and Festrotandra, due to the specifics of the landscape, the road was generally becoming the main guideline when moved. From the statement of Foreturrow Nenets: "I traveled and focused only on the road. In another place, there is a deer will not go. Without the road, deer will not go either "[PM Adareva, Tazovsky district]. The shrubs cut down in a dense shrub (PE-Dara "Ersay) became narrow corridors through which the Nenets and their deer herds took place in their nomads.
Conclusion
Navigation knowledge of the Nenets includes the richest luggage information on local geography and nature, orientation experience with the help of a whole system of various techniques, proven action algorithms with extreme situations that arise in the path of extreme situations communicated to the automatism of applying the use of all this in practice. Knowledge of natural landmarks, the use of artificial pointers, their memorization technique is the basis of directly orientation practices.
One of the most important results of this study is to conclusion about the allocation of rivers and elevations (hills, mountains, waterproof ridges) as universal and priority natural benchmarks for the tundra nonsense. The first, in fact, represent for residents
tundra A kind of coordinate network to which it is convenient to bind the location of other objects; In the winter, they often became not the most short, but reliable roads. With this, by the way, the simplified form of memorizing the configuration of the flow of watercourses is only in general, without details. The second benchmarks, hill, - like a vaccine, noticeable at a high distance, allow you to "hold" in the imagination of the entire picture of the surrounding landscape, and, in addition, are valuable in that they can be used to review the terrain.
Bibliographic list
Sources
Field materials V.N. Adaeva, 2014 (Nadym, Tazovsky district YNAO).
Field materials E.A. Volzhanina, 2014 (Yamalsky district of YNAO).
Field materials R.Kh. Rakhimova, 2014 (Nadym, Tazovsky district of YNAO).
Literature
Towns B.N. A brief essay of the population of the Far North-East of Western Siberia // Izv. Ros. geogr. o -a. T. VIII. Vol. 2. 1926. P. 50-76.
Evaven V.P. According to the tundra of Yamal to the White Island: the expedition to the extreme north of the Yamal Peninsula in 1928-1929. Tyumen: IPOS SB RAS, 1992. 282 p.
Zhitkov B.M. Peninsula Yamal. SPB: Type. MM Stasyulevich: 1913. X. 350 s.
Sources on the ethnography of Western Siberia. Tomsk: Publishing House of TSU, 1987. 284 p.
Kulemisin V.M. Spatial orientation of hunting nations // Siberia in the Millennium Panorama: Materials of the International. Simp.: in 2 tons. T. 2. Novosibirsk: Publishing House Iat SB RAS, 1998. P. 242-244.
Kulemisin V.M. On the spatial orientation of the Selkups and Khantov // Land Kolpashevskaya: Sat. sciential-popular. Essays. Tomsk: Publishing House of TSU, 2000. P. 20-212.
Kushelevsky Yu.I. North Pole and Earth Yalmal: Travel Notes. SPB: Type. M.V.D., 1868. 156 p.
Lavrille A. Orientation on rivers at the Evenkov Southeast Siberia. System of spatial, social and ritual orientation // EO. 2010. No. 6. P. 115-132.
Lebedeva A.A. On the navigation art of peoples of oceania // Indonesians and their neighbors. Festschrift E.V. Reuuenkova and A.K. Oglochelan. St. Petersburg: Mae RAS, 2008. P. 365-371.
Salinder I. Useful Science // Northern Expansions. 1987. No. 6. P. 40.
Tereshchenko N.M. Nenetsco-Russian dictionary. M.: OV. Encycle., 1965. 942 p.
Harechi G.P. Nature in the traditional worldview of the Nenets. St. Petersburg: Historical Illustration, 2012. 160 p.
Schrenk A.I. Journey to the northeast of European Russia through the Tundras Samoyov to the Northern Ural Mountains, undertaken by the highest command in 1837 by Alexander Schedule. SPB: Type. Grigory Trussov, 1855. 665 p.
Allen G.L. Principles and Practices for Communicating Route Knowledge // Applied Cognitive Psychology. 2000. No. 14. P. 333-359.
Aporta C. New Ways of Mapping: Using GPS Mapping Software to Plat Place Naments and Trails in IgLoolik (Nunavut) // Arctic. 2003. No. 4. P. 321-327.
Aporta C. The Trail As Home: Inuit And Their Pan-Arctic Network of Routes // Human Ecology. 2009. Vol. 37. P. 131-146.
Istomin K.V., Dwyer M.J. Finding The Way: (A Critical Discussion of Anthropological Theories of Human Spatial Orientation with Reference to Reindeer Herders of Northeastern Europe and Western Siberia) // Current Anthropology. 2009. Vol. 50. No. 1. P. 29-49.
Leroi-Gourhan A. Gesture and Speech. Cambridge, MA: Mit Press, 1993. 432 p.
Tyumen, IPOS SB RAS [Email Protected]
The Paper Presents a set of Earth-Based Natural and Artificial Landmarks Used by The Nenets, Together With Practice of Their Learning and Use. Subject to Consideration Being a Double-Level Landscape Knowledge AMONG The Tundra Nenets, Suggesed by K.V. Istomin and M.J. DWYER, WHERE THE UPPER LEVEL ALLOWS MOVING EASILY ACROSS THE TERRITORY, WHILE THE LOWER ONE CONTAINS A DETAILED LANDSCAPE KNOWLEDGE NECESSARY FOR REINDEER BREEDING. The Tundra Nenets Rivers And Hills Stayed The Top Priority and Universal Natural Landmarks.
Spatial Orientation, Tundra Nenets, North Landscapees, Conventional Signs, Roads.
Classification of real estate facilities Classification factor The components of the origin 1. Natural (natural) objects. 2. Artificial objects (buildings). View of 1.Name.2. Buildings.3. Constructions. 4. Enterprises. 5. Premises. 6.Nogle plant. 7. Related rights. 8.INay objects. Geographical factor 1. Local.2. Urban. Egyial. National.5. World. Functional purpose 1. Supplied land plots (for building or other objectives). 2. Natural complexes (deposits) for their operation. By the nature of the use for housing: houses, cottages, apartments; for trade and sphere of paid services; For commercial and industrial activities: hotels, office space, shops, restaurants, service points, factories, plants, warehouses; For agricultural purposes: farm, gardens; For special purposes: schools, churches, monasteries, hospitals, nursery gardens, nursing homes, buildings, governmental and administrative institutions
Classification of real estate objects The classification factor is the scale of the scale 1.The Massives. Separate land plots.3. Complexes of buildings and structures.4. Residential apartment building. Residential one-friendly house (mansion, cottage) .6. Section (entrance) .7. Floor in section.8. Apartment.9. Room 10. Summer cottage.11. Complex of administrative buildings.12. Building.13 Room or part of buildings (sections, floors) Preparedness for use 1. Ready objects. 2. Required reconstruction or overhaul. 3. Require completion of construction.

Classification of real estate objects Factor classification components for the objectives of ownership 1. For business. 2. To stay the owner. 3. As investment. 4. As inventory. 5. For mastering and development in order to consume exhaust resources. According to specialization 1. Specialized: refineries and chemical plants, museums, libraries, and similar premises belonging to the public sector. 2. Non-specialized: all other real estate on which there is universal demand for open market For investment, use in existing or similar purposes. By reproducibility 1. Landproducts: Land plots, mineral deposits. 2. Reproducible: buildings, structures, perennial plantings.

Classification of real estate objects by category A, B, C. Category Characteristics of category A objects of real estate used for business (enterprises, parts of enterprises that can be used independently; non-specialized real estate; offices, warehouses, corps, etc.) in real estate for investment Investments in order to receive income from capital investment (rent, rent, leasing, trust, mortgage, etc.) with redundant real estate issued for sale due to the inability to use it in business.

Stages of the life cycle of the real estate object Stage stage name Characteristic 1st preinvestment (analysis of the feasibility of creating, justifying efficiency) Development of the concepts of creating an object; Justification of possible options for the effectiveness of the object; determination of project financing sources; Creation technical project documentationnecessary to obtain permits and the implementation of the preparation of the land plot (with fixation of form and size, with the removal of natural and artificial vegetation, with draining water bodies); Definition of the project executor; The choice of the best and most effective way to use the real estate object, taking into account the characteristics of its characteristics and all properties of the environment. 2nd Creating an object (design, construction) Organization of facility facilities in accordance with the specifications, laying of communications, landing new plantations, preparation and commissioning.

Stages of the Life Cycle Property Object Stage Stage Name Characteristic 3rd Commissioning At this stage Operations are carried out with an object and registered by the state a change in the legal fate of the object: commissioning for its intended purpose or sale in the real estate market. When buying a sale of an object, a subject of ownership is changing. When passing the Earth or (s) improvements to the rent or the owner of the right to use (and, perhaps, possession) is transferred to another subject with the advent of importing ownership. The 4th exploitation of the object (possession and use) at this stage of the life cycle is organized by rational spending by users of the consumer potential of the object and obtaining maximum income from operation

Stages of the life cycle of the real estate object stage stage name Characteristic 5th Reconstruction and subsequent exploitation As a result of operation, the object is functionally and economically obsolete, so it is necessary to carry out overhaul (reconstruction, modernization) in order to increase income from subsequent operation. 6-ypperphylation as a result of deterioration of consumer properties, changes in functional purposes possible is possible to re-reflect the real estate object. 7th Elimination of the object The end of the economic life life. Termination of the existence of an object: Natural destruction, demolition. To minimize the liquidation costs, proposals are considered to appoint a timing and economically expedient method of demolition of buildings, the possibility of selling elements of structures and materials of liquidated buildings and communications.